Frictional unemployment goes up when:
A. Students quit work to return to school at the end of the summer.
B. A corporation transfers a worker to another city.
C. A worker quits one job in order to search for another.
D. There is inadequate demand for labor.
C. A worker quits one job in order to search for another.
You might also like to view...
Refer to the figure below. In response to gradually falling inflation, this economy will eventually move from its short-run equilibrium to its long-run equilibrium. Graphically, this would be seen as 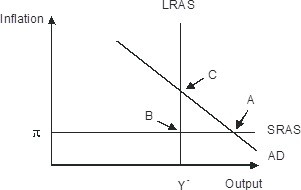
A. long-run aggregate supply shifting leftward B. Short-run aggregate supply shifting upward C. Short-run aggregate supply shifting downward D. Aggregate demand shifting leftward
In order to bring GDP and national income into accord,
a. add indirect business taxes to national income and we have GDP b. add depreciation of capital and indirect business taxes to GDP and we have national income c. subtract depreciation of capital from GDP and we have national income d. subtract depreciation of capital and proprietor's income from GDP and we have national income e. subtract depreciation of capital and indirect business taxes from GDP and we have national income
A university raises annual tuition by 10 percent. No other events have occurred, and the university's revenues have increased. It must be TRUE that
A. there was no associated change in quantity demanded. B. the associated change in quantity demanded was greater than 10 percent. C. the associated change in quantity demanded was smaller than 10 percent. D. the associated change in quantity demanded was equal to 10 percent.
Refer to the diagram, which relates to Firm A. Which of the following would shift A's average total cost curve from ATC 1 to ATC 2 ?
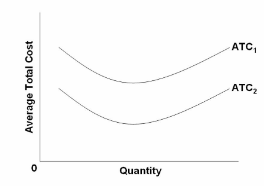
A. Replacement of old equipment with new, more productive equipment embodying technological advance.
B. A decrease in the incomes of A's customers.
C. A move along A's total product curve (not shown).
D. The increase in the price of one of the major inputs used to produce A's product.