The conventional fiscal policy to fight inflation is to ___________ while the conventional monetary policy is to ___________.
Fill in the blank(s) with the appropriate word(s).
run budget surpluses; slow the rate of monetary growth
You might also like to view...
Answer the following statement(s) true (T) or false (F)
1. A non-congested toll road is an example of a good that is excludable, but not rivalrous in consumption. 2. Public goods can frequently be provided by private action when the resulting benefits are widespread. 3. All economists agree that a public good is one the is nonrivalrous and nonexcludable. 4. When a public goods increases the desirability of living in a certain area, benefits tend to be captured entirely by an increase in land values. 5. In a Clarke tax scheme, the amount of tax that a person pays depends, in part, on his revealed preference for the public good.
The price elasticity of demand equals 1:
A. whenever the slope of a straight-line demand curve equals zero. B. at the midpoint of a straight-line demand curve. C. whenever the slope of a straight-line demand curve is greater than 1 in absolute value. D. whenever the slope of a straight-line demand curve is less than 1 in absolute value.
In graph a, why does q1 move to q2?
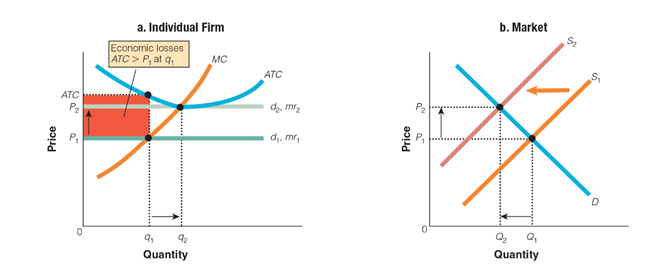
a. When firms leave the market, the demand increases for the firms remaining, causing quantity to increase for each firm.
b. When firms leave the market, the price decreases for the firms remaining, causing quantity to increase for each firm.
c. When firms leave the market, the demand decreases for the firms remaining, causing quantity to decrease for each frim.
d. When firms leave the market, the price increases for the firms remaining, causing quantity to decrease for each firm.
Jerry's Marginal Utility for consuming beer and pizza with $8.00 in income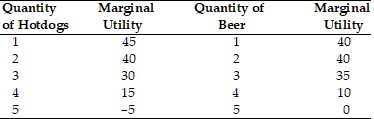 In the above table, Jerry experiences diminishing marginal utility after consuming how many hotdogs?
In the above table, Jerry experiences diminishing marginal utility after consuming how many hotdogs?
A. 1 B. 2 C. 3 D. 4