The aggregate supply curve in the classical model is
A) horizontal.
B) vertical.
C) upward sloping.
D) downward sloping.
B
You might also like to view...
From a microeconomic perspective, the relatively low U.S. household saving rate contributes to an increasing inequality of wealth resulting from:
A. the higher saving rate of low-income households. B. the higher national saving rate. C. the lower saving rate of low-income households. D. the lower national saving rate.
Products X, Y, and Z have price elasticities of 3.0, 0.80, and 1.0 respectively. Total revenue decreases if the price of
A) product X falls. B) product Y falls. C) product Z falls. D) product X or product Z falls. E) product Y or product Z falls.
The Happy Mountain Brewing Company sells ground organic coffee in one pound containers through several grocery chains in the US
The firm has two divisions: the roasting division buys raw organic coffee beans and then blends, roasts, and grinds the beans, and the merchandising division packages and distributes the ground coffee. a. Please draw a carefully labeled figure that illustrates the optimal transfer pricing policy for the firm if there is no outside market and the firm is a monopoly seller (i.e., there are no other sellers of ground organic coffee). In particular, please show the optimal transfer price that is paid to the roasting division, the optimal retail price charged by the merchandising division, and the optimal amount of coffee sold. b. Suppose poor weather conditions in South American increase the price of raw coffee beans. How does this affect the marginal cost curve for the roasting division? Does this also affect the marginal cost of merchandising (packaging and distribution)? How do the optimal transfer price, retail coffee price, and quantity sold change due to this weather problem?
A shift from D1 to D2 causes equilibrium price to __________ and quantity to __________.
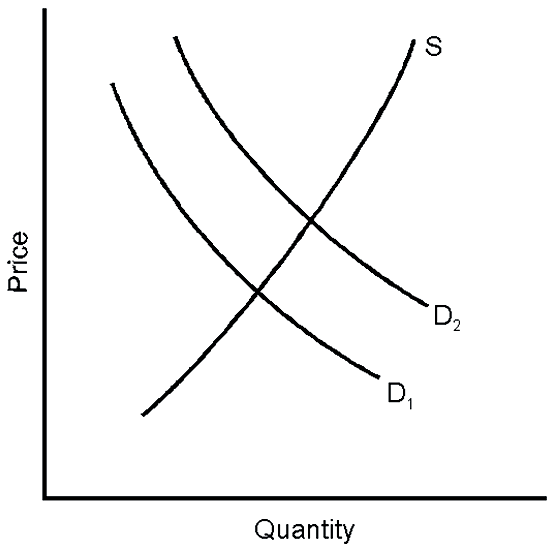
A. rise; rise
B. fall; fall
C. rise; fall
D. fall; rise