What effect does a stronger dollar have on aggregate supply? Why?
What will be an ideal response?
A stronger dollar means that U.S. residents can buy foreign goods more cheaply. Since some of the foreign goods will be raw materials and partially processed goods, input prices fall, which causes aggregate supply to increase.
You might also like to view...
Refer to the payoff matrix below. If Camp with Us is known for consistently offering special financing and this is the focal point, what is the equilibrium of the game using the focal point criterion?
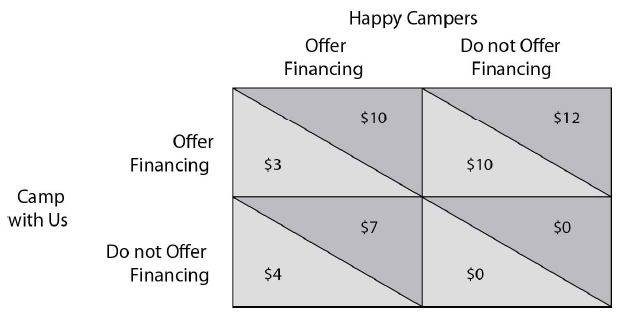
Camp with Us and Happy Campers compete in the market for campers. Each firm must decide each season if they are going to offer special financing or not. The above payoff matrix shows each firm's net economic profit at each pair of strategies.
A) Camp with Us Offer Financing and Happy Campers Do Not Offer Financing
B) Camp with Us Offer Financing and Happy Campers Offer Financing
C) Camp with Us Do Not Offer Financing and Happy Campers Do Not Offer Financing
D) Camp with Us Do Not Offer Financing and Happy Campers Offer Financing
In the short run, why would a firm in a perfectly competitive market shut down production if the prevailing market price falls below the lowest possible average variable cost?
a. At that point (economic) profit is zero. b. Below that point average revenue becomes less than marginal revenue. c. Below that point marginal revenue becomes insufficient to pay for avoidable average variable cost. d. Below that point other firms with similar cost will find it profitable to enter the market and take away demand from the existing firms.
Which of the following is a result of monopolists producing fewer goods and selling them at a higher price than perfectly competitive firms?
a. The elimination of barriers to entry b. Losses c. Diseconomies of scale d. Positive economic profits
The slope of a line is the
A) change in the values along the x-axis divided by the change in the values along the y-axis. B) values on the x-axis divided by the values on the y-axis. C) change in the values along the y-axis divided by the change in the values along the x-axis. D) values on the y-axis divided by the values on the x-axis.