If the distance between us and a star is doubled, with everything else remaining the same, its luminosity
A) is decreased by a factor of two, and its apparent brightness is decreased by a factor of two.
B) remains the same, but its apparent brightness is decreased by a factor of four.
C) is decreased by a factor of four, and its apparent brightness is decreased by a factor of four.
D) remains the same, but its apparent brightness is decreased by a factor of two.
E) is decreased by a factor of four, but its apparent brightness remains the same.
B
You might also like to view...
Flashes from unseen lightning are called ______________
Fill in the blank(s) with correct word
There are samples of two different isotopes, X and Y. Both contain the same number of radioactive atoms. Sample X has a half-life half that of Y. How do their decay rates compare?
a. The rates of X and Y are equal. b. X has a greater rate than Y. c. The rate depends on atomic number, not half-life. d. X has a smaller rate than Y.
Why do stars in the halo of the galaxy have almost no heavy elements such as carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen?
A.) Those elements have been used up in halo stars. B.) Heavy elements are biological, and there is no life out there to make them. C.) Halo stars formed before those elements were made. D.) Making C, N, and O requires massive stars, and there are no massive stars in the halo. E.) None of the above.
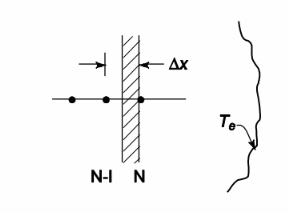
How would you treat a radiation heat transfer boundary condition for a one-dimensional steady problem? Develop the difference equation for a control volume near the boundary and explain how to solve the entire system of difference equations. Assume that the heat flux at the surface is q = ? ? (Ts4 – Te4) where Ts is the surface temperature and Te is the temperature of an enclosure surrounding the surface.
GIVEN
• Radiation boundary condition
• One-dimensional steady conduction
FIND
(a) Difference equation for control volume near surface (b) Solution method
SKETCH