The Bretton Woods system worked fairly well for a number of years, but it finally broke down over
a. lack of agreement on how to settle the problems of the surplus nations.
b. its inability to devalue the U.S. dollar.
c. the huge debts of the IMF to less-developed countries.
d. the controversies generated by surplus nations wanting to devalue their currencies.
b
You might also like to view...
Refer to the scenario above. Suppose you decide to buy a Toyota Corolla. You value the car for $10,000. You don't know it, but the car dealer values it for $8,500
If you have a zero value for poor-quality cars, what is the most that would you be willing to pay for the car? A) $3,000.50 B) $6,666.67 C) $10,000 D) $5,000
If the economy in the graph shown is currently at point D, we can conclude the:
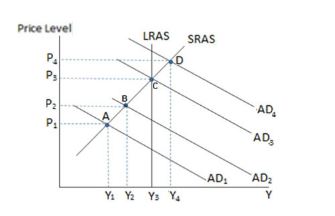
A. economy is in an economic boom.
B. government may want to enact contractionary fiscal policy.
C. unemployment rate is likely very low.
D. All of these are likely to be true.
If the production of a good generates a positive externality, then:
A. there will be deadweight loss at the market equilibrium quantity. B. production of the good is harmful. C. total economic surplus will be maximized at the market equilibrium quantity. D. the government should tax producers of the good.
Income taxes and transfer payments...
What will be an ideal response?