The rate-of-return regulated public utility has a strong profit-seeking motive
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
F In the typical case, the public utility is limited in the profit it can earn, and it can earn that profit quite easily (it is a monopoly), so it need not strive hard to seek profit.
You might also like to view...
If the indifference curves between two goods are L-shaped, the goods are
A) complementary goods. B) substitute goods. C) normal goods. D) inferior goods.
Agriculture, clothing, and textiles are singled out for treatment in the chapter because
A) they tend to be the most highly protected sectors of industrial economies. B) they tend to be the least-protected sectors internationally. C) the policies of high-income nations in these sectors may have harmful effects in low-income countries. D) A and C are both correct. E) B and C are both correct.
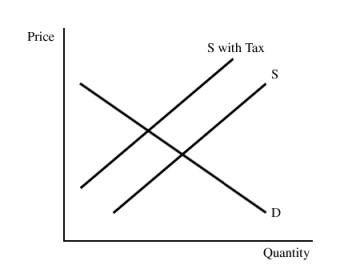 Figure 16.4The pollution tax in Figure 16.4:
Figure 16.4The pollution tax in Figure 16.4:
A. reduces equilibrium output. B. reduces pollution associated with the production of the good. C. raises equilibrium price. D. All of these
Refer to the information provided in Scenario 22.6 below to answer the question(s) that follow.SCENARIO 22.6: Following is information pertaining to four surveys:Survey 1: 50 pre-law students at Vanderbilt University are surveyed for a study to see if taking an LSAT preparation course was effective in improving their chance of being admitted to law school.Survey 2: 600 newly hired Houston-area elementary school teachers are surveyed for a study to determine how much salary they were willing to sacrifice to get a job teaching in a school with a high-quality reputation.Survey 3: 950 people are surveyed 6 months after buying a new car for a study to see how satisfied they are with their purchase.Survey 4: 75 people are surveyed in front of 5 different casinos on the Las Vegas Strip fo a
study to determine the average daily gambling budget of a Las Vegas visitor.Refer to Scenario 22.6. Of the four surveys, which is likely to be the most statistically significant? A. Survey 1 B. Survey 2 C. Survey 3 D. Survey 4