A policymaker against stabilizing the economy would be likely to believe
a. policymakers should "do no harm".
b. there are no obstacles to the practical application of policy in real life.
c. policy lags are short enough that implementing policy changes in response to recession is not too risky.
d. policy mitigates the magnitude of economic fluctuations.
a
You might also like to view...
Raghib teaches mathematics at Camford University and receives $40,000 per year. His spouse, Noraini, works as a self-employed computer programmer and charges $40 per hour. Which of the following is true?
a. Raghib's income is personal interest; Noraini's is wages b. Raghib's income is a salary; Noraini's is personal interest c. Both Raghib and Noraini receive proprietor's income d. Both Raghib and Noraini receive wage or salary income e. Raghib's income is a salary, and Noraini's income is a proprietor's income
Which of the following is correct with regard to the supply of money?
a. The money supply is inversely related to the interest rate. b. The money supply is independent of the interest rate. c. The money supply is positively related to the interest rate with a relatively flat slope. d. The money supply curve is horizontal. e. The money supply is positively related to the interest rate with a relatively steep slope.
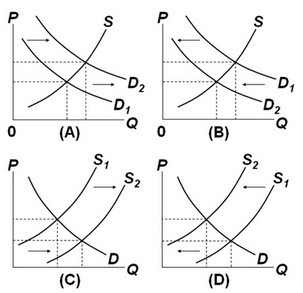 Which of the above diagrams illustrate(s) the effect of an increase in the price of Budweiser beer on the market for Coors beer?
Which of the above diagrams illustrate(s) the effect of an increase in the price of Budweiser beer on the market for Coors beer?
A. A only B. B only C. C only D. A and C
Suppose a consumer is currently buying 5 goods so that utility is maximized. The price of one of the goods falls while the prices of the other 4 goods do not change. The consumer should
A. buy less of all goods being consumed to get to the optimal position. B. buy more of the good that has experienced the fall in price to get to the optimal position. C. buy more of all goods being consumed to get to the optimal position. D. buy more of all of the goods but the one that experiences the decline in price, to get to the optimal position.