Refer to Figure 10-2. Which of the following statements is true?
A) Points a and b may not necessarily be the utility-maximizing quantities of ice cream cones at two different prices because we have no information on the consumer's budget or the price of other goods.
B) Points a and b are derived independently of the utility-maximizing model.
C) Points a and b are the utility-maximizing quantities of ice cream cones at two different prices of ice cream.
D) Point a could be a utility-maximizing choice if the price is $3 but point b may not be because we have no information on the marginal utility per dollar when price changes.
C
You might also like to view...
The supply curve for land in New York City is most likely
A) horizontal or perfectly elastic. B) a downward sloping straight line. C) an upward sloping straight line. D) vertical or perfectly inelastic.
A perfectly competitive market is one in which:
A. fully informed, price-taking buyers and sellers easily trade a standardized good or service. B. fully informed, price-making buyers and seller easily trade a standardized good or service. C. uninformed, price-taking buyers and sellers easily trade a standardized good or service. D. uninformed, price-making buyers and seller easily trade a standardized good or service.
If the graph shown is displaying a competitive market and the market is currently offering a wage more than P*:
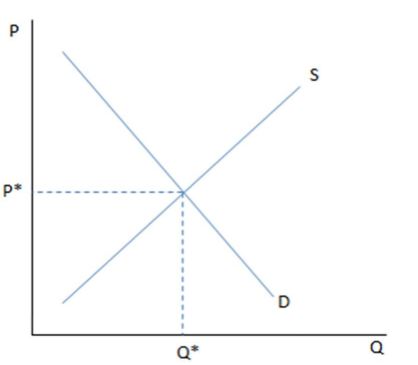
A. there would be a surplus of workers who want to work at that wage.
B. there would not be unemployment in the market.
C. firms would have a hard time finding workers.
D. equilibrium would be achieved.
If demand is perfectly elastic, then
a. the demand curve is a horizontal line b. supply is perfectly inelastic c. supply is perfectly elastic d. the demand curve is a vertical line e. the demand curve is downward sloping