________ determine(s) which products have been produced within a free-trade area and which products have been produced outside the area and therefore are subject to trade barriers.
A. Rules of origin
B. Trade diversion
C. The most favored nation principle
D. Trade creation
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
Suppose there are two goods: guns and roses. Also suppose Australia is initially closed to trade. When international trade is opened, Australia chooses to sell guns and buy roses in the world markets.
(i) Which is higher, Australia's autarkic relative price of guns or the world relative price of roses? (ii) If the world relative price of guns falls, will Australia be better off or worse off? What if the world relative price of guns rises? Explain.
Use the figure below to answer the following question.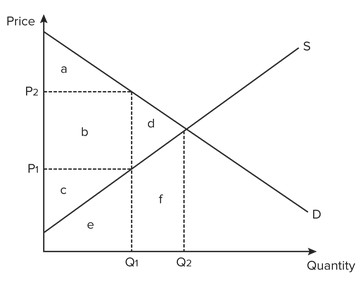 If actual production and consumption occur at Q1 and the price is P2
If actual production and consumption occur at Q1 and the price is P2
A. deadweight loss equals area f. B. producer surplus equals area c. C. producer surplus equals area c + b. D. consumer surplus equals area a + b.
Which of the following features is common to both perfectly competitive markets and monopolistically competitive markets?
A. Firms produce homogeneous goods. B. There is free entry. C. There is free entry and long-run profits are zero. D. Long-run profits are zero.
When output increases by 1%, the number of jobs does not tend to rise by 1% in the short run. Which of the following statements represents one of the reasons why this is true?
A. Firms are likely to meet some of the increase in output by reducing labor productivity. B. A firm is likely to meet some of the increase in output by decreasing the number of hours worked per job. C. Firms are likely to meet part of the increase in output by eliminating any excess capital they may have. D. A firm is likely to meet some of the increase in output by increasing the number of hours worked per job.