When people cannot be excluded from consuming a good, even if they have not paid for the good, competitive markets would
A) produce more of the good than society needs.
B) allocate more resources than the efficient amount to the production of the good.
C) produce the good so that people could enjoy a "free ride."
D) produce less than the efficient quantity.
E) eliminate the deadweight loss.
D
You might also like to view...
Individuals play ____ in causing pollution
a. almost no role b. a large but decreasing role c. a major role d. a reconstructive role
When the government imposes a barrier to entry in a market,
a. more resources will be wasted by firms attempting to secure and maintain market power. b. the options available to consumers will increase in the protected market. c. allocative efficiency will be improved by the reduction of wasteful competition. d. consumers will be better able to direct the smaller number of producers to serve their interests.
The National Labor Relations Act of 1935 is also known as the ______.
a. Landrum-Griffen Act b. Social Security Act c. Taft-Hartley Act d. Wagner Act
In this graph for negative externalities in production, the efficient equilibrium point is at ______.
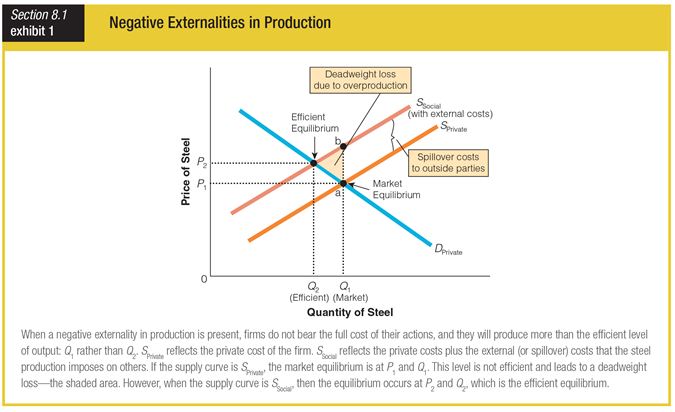
a. point A
b. point B
c. P1 and Q1
d. P2 and Q2