Explain how planetary nebulae and white dwarfs are related to mass loss from an aging medium-mass star
What will be an ideal response?
When a main sequence star becomes a red giant, the outer layers are loosely held by gravity. This allows the star to lose significant amounts of mass through a strong stellar wind. This mass loss is increased during helium shell burning, when unstable conditions can cause the core energy generation to flare.The mass loss creates an expanding shell or shells of hydrogen gas moving away from the star. If the object left in the center of the expanding shell is hot enough, the gas will become ionized and glow with hydrogen emission forming a planetary nebula.After the outer layers of the star are ejected, the remaining core is not hot enough to sustain fusion. It contracts, becoming a small, hot object known as a white dwarf.
You might also like to view...
A thin spherical shell of radius 20.0 cm has 5.0 ?C of charge uniformly distributed over its surface. What is the magnitude of the electric field 2.00 m from the center of the sphere?
a. 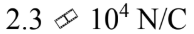
b. 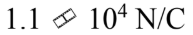
c. 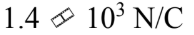
d. 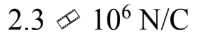
e. 0
How do we think the first generation of stars would have been different from stars born today?
A) They would have lacked elements heavier than hydrogen and helium. B) They would have generated energy through fission rather than fusion. C) They would have all been very low in mass. D) They would have shined only with ultraviolet light, not visible light.
In air and in water the same sound travels with different
A) frequencies. B) speeds. C) both of these D) neither of these
It is difficult to use light from distant galaxies to compute the true physical distance to those galaxies today because the Universe has expanded since it was emitted.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)