Vertical integration often aims to
a. Prevent the retailers from defeating upstream price discrimination through arbitrage
b. Avoid paying higher taxes
c. Serve as a "signal" of the manufacturer's belief of the likely success of his product
d. All of the above
d
You might also like to view...
Someone who is risk-preferring has
A) diminishing marginal utility of wealth. B) constant marginal utility of wealth. C) increasing marginal utility of wealth. D) less marginal utility of wealth than someone who is risk-preferring.
A decrease in demand with the supply held constant leads to:
a. an increased equilibrium price and an increased equilibrium quantity. b. a decreased equilibrium price and a decreased equilibrium quantity. c. a decreased equilibrium price and an increased equilibrium quantity. d. an increased equilibrium price and a decreased equilibrium quantity.
To answer the question, refer to the following table showing a demand schedule: 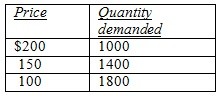 If price falls from $200 to $150,
If price falls from $200 to $150,
A. an arrow representing the price effect points down and is longer than an arrow for the quantity effect. B. an arrow representing the quantity effect points up and is shorter than an arrow for the price effect. C. arrows representing the price and quantity effects both point down. D. total revenue moves in the same direction as the arrow representing the quantity effect. E. arrows representing the price and quantity effects both point up.
Suppose that Dairy Barn Foods produces a regular sour cream with 10 grams of fat per serving and a "low fat" sour cream with only 5 grams of fat per serving (assume that this is still considered a lot of fat to consume per serving). According to prospect
theory, how should Dairy Barn promote its "low fat" sour cream? A. It should make no mention of fat content, either in absolute terms or relative to its regular sour cream. B. It should advertise that the "low fat" sour cream has only "half the fat" of the regular sour cream. C. It should advertise that the "low fat" sour cream has only 5 grams of fat per serving. D. It won't matter what strategy Dairy Barn uses, as consumers are sufficiently informed as to not be affected by the advertising.