How can a nation and its producers determine whether or not it has a comparative advantage in producing a particular good or service?
What will be an ideal response?
Whether a nation has a comparative advantage in the production of a particular good or service can be determined by comparing the price the good or service sells for domestically to the world price of the same good or service. If the domestic price is less than the world, the nation has a comparative advantage in the production of that good or service. If the domestic price exceeds the world price, the nation does not have a comparative advantage in the production of that good or service.
You might also like to view...
Refer to Variable Cost of Production. If the total cost of producing the sixth unit of output is $190, fixed costs must be
The following questions refer to the following table which shows a firm's variable costs of production.
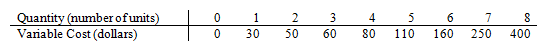
a. $8.
b. $22.
c. $30.
d. $40.
The practice of making choices using generalizations based on observable characteristics like race, gender, or age is called:
A. discrimination. B. means-testing. C. conditional cash transfers. D. None of these is true.
The difference between a change in quantity supplied and a change in supply is that a change in:
a. quantity supplied is caused by a change in a good's own, current price, while a change in supply is caused by a change in some other variable, such as input prices, prices of related goods, expectations, or taxes. b. supply is caused by a change in a good's own, current price, while a change in the quantity supplied is caused by a change in some other variable, such as input prices, prices of related goods, expectations, or taxes. c. quantity supplied is a change in the amount people want to sell, while a change in supply is a change in the amount they actually sell. d. supply and a change in the quantity supplied are the same thing.
The level of money income below which a family is considered poor is called the
a. bottom 20 percent of the income distribution. b. poverty threshold income level. c. guaranteed income level. d. subsistence income level.