In the diagram below, the importance of the falling precipitation at "A" for the global carbon cycle is that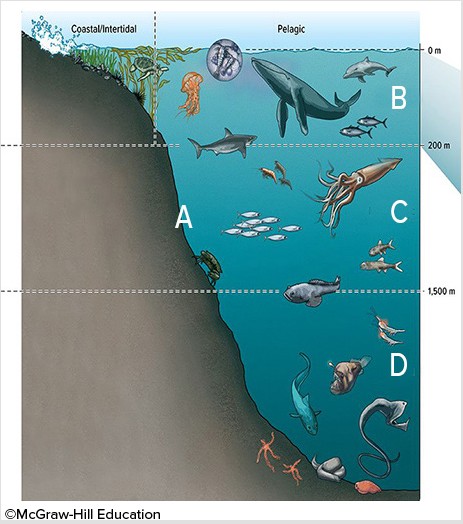
A. the falling rain lubricates the Earth's surface, making crustal deformation more likely, which would bring carbon stored in the lithosphere back up to the atmosphere, warming the Earth.
B. the falling rain makes carbon in the atmosphere more inert-giving it much greater potential to act as a greenhouse gas and warm the Earth.
C. the falling rain brings CaCO3 which was trapped in the atmosphere to the surface, cooling the Earth.
D. CO2 combines with water to form H2CO3, removing carbon from the atmosphere and cooling the Earth.
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
Country A has approximately 100,000 children between the ages of 0 and 14, although it has a high infant mortality rate It also has 202,000 elderly people who have retired from work, although most continue to live in multi-generational households with their children and grandchildren. Country A also has 310,000 people who can participate in the workforce. We can use these data to calculate that the
A) dependency ratio is about 50 percent. B) life expectancy ratio is about 50 percent. C) population ratio is high. D) dependency ratio is about 67 percent. E) dependency ratio is about 33 percent.
During the Pleistocene ice age:
a. all of Earth's fresh water was frozen. b. glaciers occupied the Amazon River basin. c. sea level was lower than it is today. d. the Antarctic ice sheet was smaller than it is today. e. Greenland was a driftless area.
Which of the following best defines temperature?
A) The amount of heat energy required to raise the temperature of a substance by 1 degree Celsius. B) The direct measure of the average kinetic energy of a substance's molecules. C) The energy needed to break the intermolecular bonds that hold molecules in place. D) The energy transfer from one body to another due to a difference in temperature. E) Weak interactions that become significant when molecules are very close together.
What city is the first slated to be a "solar city" with 10% renewable energy?
A) Mumbai B) New Delhi C) Agra D) Bangalore E) Varanasi