If Slick Shades has a constant marginal cost of production equal to $80 and the distributors have a constant marginal cost of distribution equal to $30, what is the profit-maximizing number of sunglasses (in hundreds) for Slick Shades to produce?
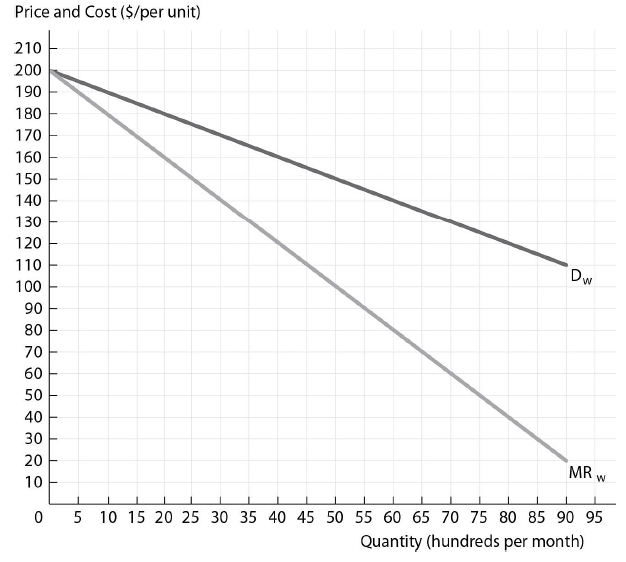
The figure above shows the wholesale demand and marginal revenue curves for Slick Shades Sunglasses, a sunglasses firm with market power. Slick Shades Sunglasses has a constant marginal cost of production and it sells to perfectly competitive independent retail distributors that have a constant marginal cost of distribution.
A) 40
B) 80
C) 55
D) 60
D) 60
You might also like to view...
Full employment corresponds to
A) equilibrium in the labor market, with actual GDP being equal to potential GDP. B) labor demand being greater than labor supply and actual GDP being equal to potential GDP. C) being at the point where the marginal product of labor equals zero. D) equilibrium in the labor market, and actual GDP exceeding potential GDP.
Net interest payments by the government are usually
A) small and sometimes negative for both the federal, and state and local governments. B) small and sometimes negative for the federal government, but large and positive for state and local governments. C) small and sometimes negative for state and local governments, but large and positive for the federal government. D) large and positive for both the federal, and state and local governments.
Assuming that there are NO income taxes, if both autonomous taxes, and government expenditures were to rise by $100 million, we would expect equilibrium GDP to
A) rise by $100 million. B) rise, but by a multiple of $100 million. C) rise by less than $100 million. D) remain unaffected because leakages have changed by the same amount.
Net public debt is the
A) difference between tax revenues and government expenditures each year. B) sum of accumulated government deficits and surpluses held by individuals and businesses and foreign institutions. C) sum of accumulated government deficits and surpluses held by U.S. government agencies. D) sum of accumulated government deficits and surpluses held by large money center banks.