The study of individual choice and its implications for the behavior of prices and quantities in individual markets is:
A. macroeconomics.
B. the Scarcity Principle.
C. microeconomics.
D. a normative economic principle.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
The marginal social cost curve ________ when production involves negative externalities
A) is parallel to the horizontal axis B) is parallel to the demand curve C) lies above the supply curve D) lies to the right of the supply curve
The producer surplus on a unit of a good is the
A) difference between the marginal social benefit and the marginal social cost. B) number of dollars' worth of other goods and services forgone to produce this unit of the good. C) difference between the price of the good and the marginal cost of producing the good. D) difference between the total cost of the good and the marginal cost.
This table shows the demand and supply schedule of a good.
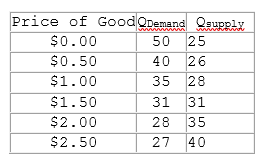
According to the table shown, at a price of $0.50 quantity demanded:
A. exceeds quantity supplied and a shortage exists.
B. is less than quantity supplied and a shortage exists.
C. exceeds quantity supplied and a surplus exists.
D. is less than quantity supplied and a surplus exists.
A perfectly inelastic demand means:
A. consumers will change the quantity they purchase when price changes. B. demand will drop to zero if the price increases by any amount. C. consumers will not change the quantity they purchase when price changes. D. the demand curve is perfectly horizontal.