Assume that a Chrysler automobile sells for $15,000 in the United States and that the exchange rate is $1 = €1.3 . For purchasing power parity to hold, the same car should sell in Germany for:
a. €15,000.
b. €11,538.
c. €19,500.
d. €1,538.
e. €15,500.
c
You might also like to view...
Explain the output and factor substitution effects of an increase in the price of capital on theDemand for labor by a firm that produces output using both capital and labor
What will be an ideal response?
As a result of the government procurement policy in the U.S.:
a. the domestic consumers are required to pay a higher price than the government for the domestically produced goods. b. the government wields the sole authority of importing goods from abroad. c. the government wields the sole authority of exporting goods. d. the government is required to buy the domestic goods if the domestic price is less than the world price. e. the government is required to sponsor research and development for the domestic firms.
In which of the following ways is graph A different from graph B?
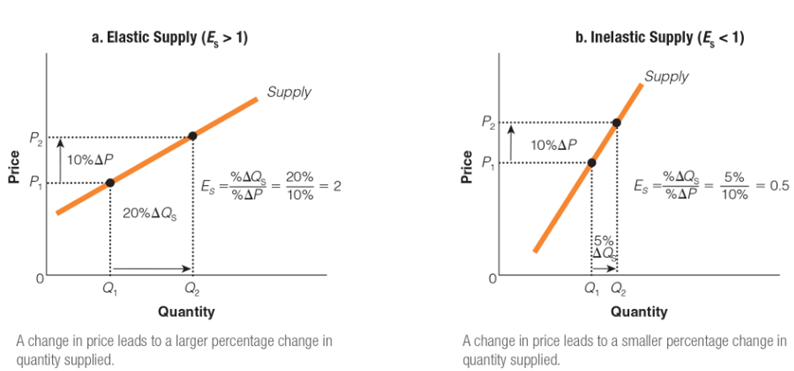
a. P1 to P2 is larger in graph B than in graph A.
b. Q1 to Q2 is larger in graph B than in graph A.
c. P1 to P2 is larger in graph A than in graph B.
d. Q1 to Q2 is larger in graph A than in graph B.
Suppose that a firm's legal staff concludes that a new production process that the firm is developing is patentable. Graphically, this new information would shift the firm's expected-rate- of-return curve on R&D to the:
A. right and reduce its optimal amount of R&D. B. right and increase its optimal amount of R&D. C. left and increase its optimal amount of R&D. D. left and reduce its optimal amount of R&D.