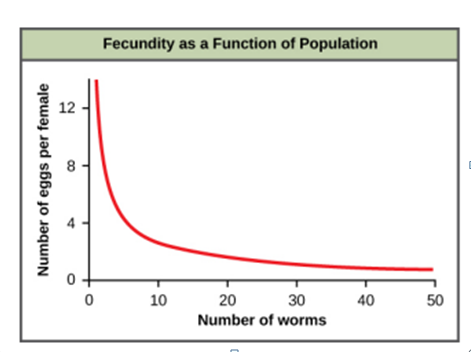
An example of density-dependent regulation is shown in this graph with results from a study focusing on the giant intestinal roundworm (Ascaris lumbricoides), a parasite of humans and other mammals. Denser populations of the parasite contained fewer eggs. One possible explanation for this is that females would be smaller in more dense populations (due to limited resources) and that smaller females would have fewer eggs. This hypothesis was tested and disproved in a 2009 study which showed that female weight had no influence. Given that each female was producing fewer eggs, why was the population continuing to grow?
a. More worms were moving in from adjacent populations.
b. The population was expanding due to increased mating.
c. With lower population densities, mortality decreased.
d. Lifespans were extending due to lower egg production.
c. With lower population densities, mortality decreased.
You might also like to view...
What is the main method of spore dispersal in the basidiomycetes?
a. Wind b. Amphibians c. Water d. Insects e. Mammals
Discuss the phenomena of immunological tolerance and autoimmune disease
What will be an ideal response?
Glucose and fructose
a. can be ring forms. b. are structurally different. c. are monosaccharides. d. have the same atoms in the same ratio. e. all of these
The short arm of a submetacentric chromosome is symbolized as the ____________________ arm. Fill in the blank(s) with the appropriate word(s)