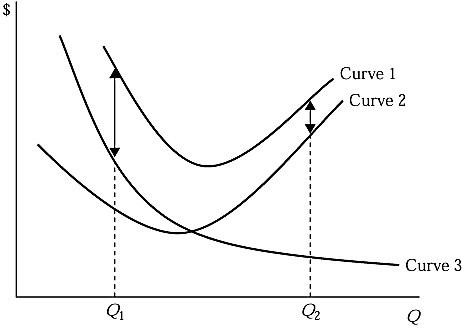
 Refer to Figure 5.2, which shows a family of average cost curves. The average fixed cost at a given level of output is represented by:
Refer to Figure 5.2, which shows a family of average cost curves. The average fixed cost at a given level of output is represented by:
A. the vertical distance between Curve 1 and Curve 2 at a given level of output.
B. the vertical distance between Curve 1 and Curve 3 at a given level of output.
C. the vertical sum of Curve 1 and Curve 2 at a given level of output.
D. the vertical sum of Curve 1 and Curve 3 at a given level of output.
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
With no Ricardo-Barro effect, a government budget surplus
A) decreases the demand for loanable funds and increases the real interest rate. B) increases the demand for loanable funds and lowers the real interest rate. C) increases the supply of loanable funds and lowers the real interest rate. D) increases the demand for loanable funds and raises the real interest rate. E) decreases the supply of loanable funds and lowers the real interest rate.
If a nation's population grows at 2 percent and its real GDP grows at 4 percent, what is the growth rate of real GDP per person?
What will be an ideal response?
Past expenses are irrelevant to supply decisions, because
A) expenses incurred in the past never affect the opportunities available in the present. B) it is essential to avoid bankruptcy. C) no one remembers the past. D) supply decisions depend on opportunities that will have to be forgone, not opportunities already forgone.
If the official settlements account is zero, whenever the United States has a current account deficit, it must also have a capital account deficit
Indicate whether the statement is true or false