Bar One has a Young's modulus that is bigger than that of Bar Two. This indicates Bar One
a. is longer than Bar Two.
b. has a greater cross-sectional area than Bar Two.
c. has a greater elastic limit than Bar Two.
d. is made of material that is different from Bar Two.
d
You might also like to view...
What observational evidence supports the idea that Mercury once shrank by some 20 kilometers in radius?
A) the presence of many impact craters B) the characteristics of the Caloris Basin C) Mercury's unusually high density D) the presence of many long, tall cliffs
Adding BCC elements such as vanadium to titanium _________the ?-phase transus.
Fill in the blank(s) with the appropriate word(s).
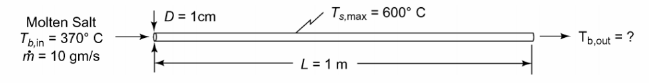
A solar thermal central receiver generates heat by focusing sunlight with a field of mirrors on a bank of tubes through which a coolant flows. Solar energy absorbed by the tubes is transferred to the coolant which can then deliver useful heat to a load. Consider a receiver fabricated from multiple horizontal tubes in parallel. Each tube is 1-cm-ID and 1-m-long. The coolant is molten salt which enters the tubes at 370°C. Under start-up conditions, the salt flow is 10 gm/s in each tube and the net solar flux absorbed by the tubes is 104 W/m2. The tube wall material will tolerate temperatures up to 600°C. Will the tubes survive start-up? What is the salt outlet temperature?
GIVEN
• Molten salt flowing through a horizontal tube that is absorbing solar energy
• Tube inside diameter (D) = 1 cm = 0.01 m
• Tube length (L) = 1 m
• Entering salt temperature (Tb,in) = 370°C
• Start-up mass flow rate (m) = 10 gm/s = 0.01 kg/s
• Net solar energy absorbed by the tube (qs) = 104 W/m2
• Maximum tube wall temperature (Ts) = 600°C
FIND
(a) Salt outlet temperature (Tb,out)
(b) Will the tubes survive start-up?
SKETCH
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
for molten salt at 370°C
Specific heat (c) = 1629 J/(kg K)
What was the last geological period in Earth's history during which the dinosaurs lived?
A) The Cretaceous Period B) The Tertiary Period C) The Triassic Period D) The Carboniferous Period