Use the Great Recession of 2007–2009 to describe the paradox of thrift.
What will be an ideal response?
During the Great Recession of 2007–2009 there was a “reverse wealth effect” because as wealth declined during the recession, people consumed less and saved more. Such a situation creates a paradox of thrift in which more saving helps individual household budgets, but as people cut back on their consumption and increase their saving, the collective effect on the economy is an adverse one that worsened the recession.
You might also like to view...
If you were building a macroeconomic model that explores the effect of the increase in interest rates on the inflation rate in Great Britain, interest rates would be an ________ variable and the inflation rate would be an ________ variable
A) endogenous; endogenous B) endogenous; exogenous C) exogenous; exogenous D) exogenous; endogenous
If the economy is represented in the graph shown and is currently at point E2, which action is the Fed most likely to undertake?
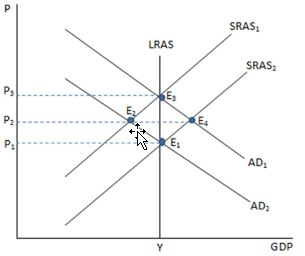
A. Expansionary monetary policy, because it will shift AD to the right.
B. Contractionary monetary policy, because it will shift AD to the left.
C. Expansionary monetary policy, because it will shift AD to the left.
D. Contractionary monetary policy, because it will shift AS to the right.
Among the following situations, which one is least likely to apply to a monopolistically competitive firm?
a. profit is positive in the short run b. total cost exceeds total revenue in the short run c. profit is positive in the long run d. total revenue equals total cost in the long run
The price of coffee increases. Which of the following is NOT part of the likely chain of events that follows from this price change?
A) Some coffee consumers reduce their consumption of coffee. B) Coffee producers increase their production of coffee. C) The producers of coffee beans increase production. D) The manufacturers of coffee machines lay off some workers.