Suppose that the economy is at an inflation rate such that unemployment is above the natural rate. How does the economy return to the natural rate of unemployment if this lower inflation rate persists? Use sticky-wage theory to explain your answer
If unemployment is above its natural rate, then actual inflation is less than expected inflation. According to sticky-wage theory, when inflation is less than expected, prices will have risen less than nominal wages which are based on expected inflation. Because prices have risen less than nominal wages, firms will choose to reduce production and lay off or fire workers. Eventually workers and firms will have lower inflation expectations and the nominal wage will adjust to a level consistent with lower inflation expectations which will encourage firms to raise production. This increase in production causes unemployment to fall and shifts the short-run Philips curve to the left and the unemployment rate will return to it natural rate.
You might also like to view...
The 'WHAT goods and services does the US produce' question can best be answered using data about which of the following?
A. Productivity. B. The distribution of GDP among different income quintiles. C. Per capita GDP. D. The distribution of output in markets, specifically among manufacturing, services, and agricultural sectors.
What do economists mean by "reverse engineering"?
A. A modification of old technology B. Taking a product apart in order to copy its design C. A decision to adopt an old technology rather than a new one D. Modification of existing machines so that they can be run by handicapped persons
Refer to the information provided in Figure 2.4 below to answer the question(s) that follow.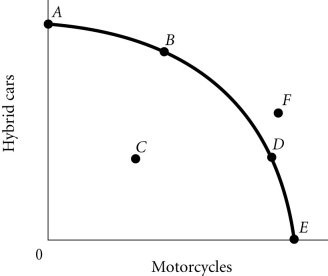 Figure 2.4According to Figure 2.4, as the economy moves from Point A to Point E, the opportunity cost of motorcycles, measured in terms of hybrid cars
Figure 2.4According to Figure 2.4, as the economy moves from Point A to Point E, the opportunity cost of motorcycles, measured in terms of hybrid cars
A. remains constant. B. decreases. C. initially increases, then decreases. D. increases.
Dumping of goods abroad:
A. constitutes a general case for permanent tariffs. B. may be part of a firm's price discrimination strategy. C. may be part of a nation's strategy to rectify its trade deficit. D. drives up prices of the dumped goods.