Explain how the marginal revenue product of labor is affected by the competitiveness of the market for goods that labor produces
In the perfectly competitive market, P = MR, so that MRP = MPP × P = MPP × MR. In less competitive
markets, P > MR, so that (MRP = MPP × P) > (MRP = MPP × MR). This explains why in less
competitive markets fewer laborers are hired than in perfectly competitive markets.
You might also like to view...
Each year, the president must submit a budget proposal to Congress by:
a. October. b. July. c. January. d. April.
The estimated demand for a good is 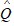 = 25 - 5P + 0.32M + 12PRwhere Q is the quantity demanded of the good, P is the price of the good, M is income, and PR is the price of related good R. This good and the related good R are
= 25 - 5P + 0.32M + 12PRwhere Q is the quantity demanded of the good, P is the price of the good, M is income, and PR is the price of related good R. This good and the related good R are
A. complements since the coefficient on M is positive. B. substitutes since the coefficient on M is positive. C. substitutes since the coefficient on PR is positive. D. complements since the coefficient on PR is positive.
The budget line shows
a. different levels of consumption associated with different levels of incomes. b. the affordable combinations of goods and services you can buy with your income. c. different levels of inputs needed to produce specific level of output. d. none of the above.
If a competitive firm can sell its product at $1,600 per unit and the marginal cost of the firm is MC = 1,100 + 2Q, then the firm will produce
A. 1,084 units. B. 160 units. C. 1,100 units. D. 250 units.