Why do nocturnal animals usually have large pupils in their eyes? How is that related to the way astronomical telescopes work?
What will be an ideal response?
Large pupils of nocturnal animals allow more light to be gathered. Likewise, telescopes with large primaries gather more light and are able to study fainter objects.
You might also like to view...
Satellite Motion:?MassRadiusOrbital radiusOrbital periodMoon A4.0 × 1020 kgunknown2.0 × 108 m4.0 × 106 sMoon B1.5 × 1020 kg2.0 × 105 m3.0 × 108 munknownMithra is an unknown planet that has two moons, A and B, in circular orbits around it. The table summarizes the hypothetical data about these moons. What is the mass of Mithra? (G = 6.67 × 10-11 N ? m2/kg2)
A. 1 × 1022 kg B. 3 × 1022 kg C. 1 × 1023 kg D. 3 × 1023 kg E. 1 × 1024 kg
Figure Q6.15 below shows a sequence of Stern–Gerlach devices. By analogy to the cases discussed in the chapter, what do you think are the probabilities that an electron entering the last device will come out of that device’s plus and minus channels, respectively? 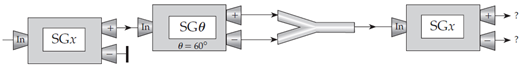
A. 1 and 0, respectively (AA if reversed, i.e., 0 and 1)
B. 0.933 and 0.067, respectively (BB if reversed)
C.  , respectively (CC if reversed)
, respectively (CC if reversed)
D. 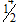 for both channels
for both channels
E. Some other probabilities (specify)
If the average velocity is non-zero over a time interval, does this mean that the instantaneous velocity is never zero over that same time interval?
A. Yes B. No
The Bohr model pictures a hydrogen atom in its ground state as a proton and an electron separated by the distance a0 = 0.529 × 10^-10 m. The electric potential created by the proton at the position of the electron is
a. -13.6 V. b. +13.6 V. c. -27.2 V. d. +27.2 V. e. +5.12 × 10^9 V.