When considering choice architecture, a nudge:
A. can sometimes accomplish public policy goals in a less expensive way than traditional methods.
B. presents choices that are similar to participants' ideal choices, but are slightly better than them.
C. is a deliberate push by choice architect to get all people to behave a certain way.
D. allows participants to choose among only choices that are good for them.
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
In the indifference curve-budget line model of labor supply,
a. labor is measured along the horizontal axis and leisure is measured along the vertical axis. b. labor is measured along the horizontal axis and consumption is measured along the vertical axis. c. consumption is measured along the horizontal axis and labor is measured along the vertical axis. d. consumption is measured along the horizontal axis and leisure is measured along the vertical axis.
In a shopping mall in a large city, the Rudolph the Reindeer store sells only merchandise for the Christmas holiday season. Most of the store's revenue and profit are attributable to the months of October, November, and December. However, the store is open throughout the year. If the owner of the store is rational, what criterion does he or she use in deciding to keep the store open year-round?
Which of the following statements describes what most likely occurred in this economy?
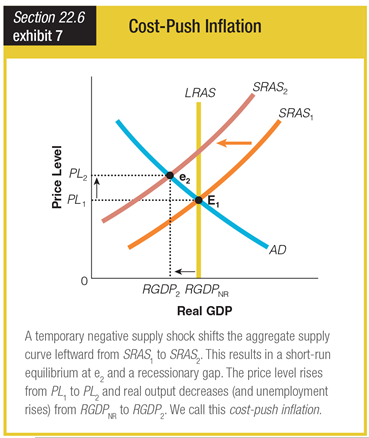
a. Unemployment fell below the natural rate of unemployment.
b. There was a temporary negative shock to demand-side forces.
c. A rightward shift in SRAS caused an inflationary gap.
d. An increase in input prices caused a recessionary gap.
Refer to the diagrams. The demand for Firm B's product is:
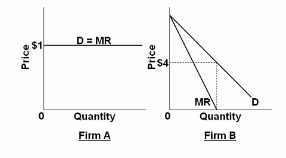
A. perfectly elastic over all ranges of output.
B. perfectly inelastic over all ranges of output.
C. elastic for prices above $4 and inelastic for prices below $4.
D. inelastic for prices above $4 and elastic for prices below $4.