Describe, in general terms, the strategy of monetary policy, explaining how monetary-policy tools are used to achieve the goals of monetary policy. What intermediate stages are important in going from tools to goals? What are the links between the different stages? How does the Federal Reserve use this strategy today?
What will be an ideal response?
The Fed uses its tools to influence intermediate targets that in turn affect the goal variables. The link between tools and intermediate targets is an economic relationship such as the money multiplier, which relates changes in the monetary base to changes in the money supply. The link between intermediate targets and the goal variables is an economic model. Today the Fed targets the Fed funds rate fairly directly, but watches many indicators to figure out the correct funds rate.
You might also like to view...
What is the law of one price?
What will be an ideal response?
In the short run, a perfectly competitive firm
A) must make an economic profit. B) must incur an economic loss. C) must make zero economic profit. D) might make an economic profit, zero economic profit, or incur an economic loss. E) None of the above answers is correct.
Refer to Scenario 1 . If you start the course in such a way that each exam score is worse than your previous average what should happen to your average score? What would happen to your average if the next exam score was larger than your previous exam
score? Explain.
According to the graph shown, if this economy were to open to trade, domestic producers would have to cut:
This graph demonstrates the domestic demand and supply for a good, as well as the world price for that good.
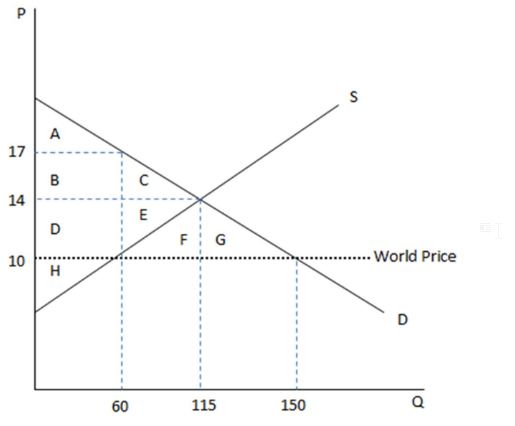
A. production by 55 units.
B. production by 90 units.
C. prices by $3.
D. prices by $7.