Which statement regarding graded potentials is false?
a. they are decremental.
b. they travel only short distances.
c. they are self-propagating.
d. they may contribute to the development of an action potential.
e. they travel in both directions along the membrane.
C
You might also like to view...
Identify the process featured in the image.
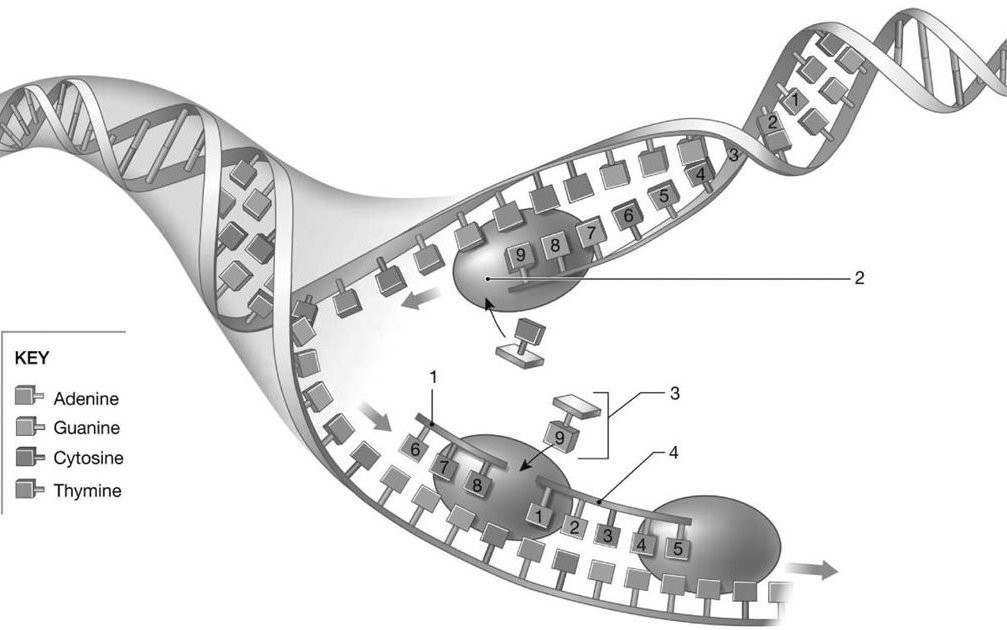
A) translation
B) replication
C) transcription
D) mitosis
E) meiosis
Small molecules, such as water and many ions, cross the membrane without assistance from the cell. This movement is called ________ and requires NO energy expenditure by the cell
A) passive transport B) active transport C) facilitated diffusion D) None of the listed responses is correct.
Explain adaptation, and differentiate between peripheral adaptation and central adaptation
A) Adaptation is an increase in receptor sensitivity in the presence of constant stimulation. Peripheral adaptation reduces the amount of information sent to the CNS. In central adaptation, the awareness of the stimulus virtually disappears. B) Adaptation is a decrease in receptor sensitivity in the presence of constant stimulation. Peripheral adaptation reduces the amount of information sent to the CNS. In central adaptation, the awareness of the stimulus virtually disappears. C) Adaptation is an increase in receptor sensitivity in the presence of constant stimulation. Peripheral adaptation increases the amount of information sent to the CNS. In central adaptation, the awareness of the stimulus is enhanced. D) Adaptation is a decrease in receptor sensitivity in the presence of constant stimulation. Peripheral adaptation increases the amount of information sent to the CNS. In central adaptation, the awareness of the stimulus is enhanced. E) Adaptation is a decrease in receptor sensitivity in the presence of constant simulation. In peripheral adaptation, the awareness of the stimulus virtually disappears. Central adaptation reduces the amount of information received by the CNS.
The foot is in which region?
A. Lumbar B. Pectoral C. Pedal D. Brachial