How does the multiplier work and what might government use it for?
The initial purchase of goods or services (by government) results in income for the recipient, who in turn spends much of that income, but generally not all of it. This sets off a chain of actions based on each spending event results in an income event for someone else, who in turn spends some percentage of the dollars (even though the dollar amounts are shrinking).
Government may use this knowledge to target its spending in ways or places that lead to a boost in aggregate demand, creating a new short-run equilibrium at a higher level of real output.
You might also like to view...
The tax multiplier is smaller in absolute value than the government purchases multiplier because some portion of the
A) decrease in taxes will be saved by households and not spent, and some portion will be spent on imported goods. B) increase in government purchases will be saved by households and not spent, and some portion will be spent on imported goods. C) decrease in taxes will be saved by households and not spent, and some portion will be spent on consumer durable goods. D) increase in government purchases will be saved by households and not spent, and some portion will be spent on consumer durable goods.
Most of the migration in the world involves people who are moving from countries with relatively ____ GDP per capita to countries with relatively _____ GDP per capita.
a. high; low b. low; low c. low; high d. high; high
Refer to the graph below, which shows the demand and supply of tickets for a Broadway play. When the play's producers take fairness into account, which of the following would most likely to occur?
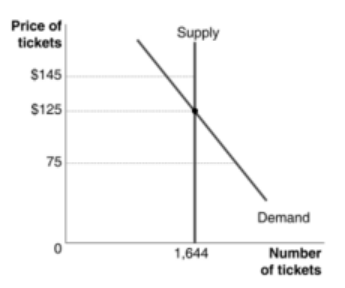
a. The market price will equal the equilibrium of $125.
b. Producers will charge $75 for a ticket even though the result would be a shortage.
c. Producers will charge $145 for a ticket in anticipation of stronger demand.
d. Producers will raise ticker prices gradually as demand strengthens over time.
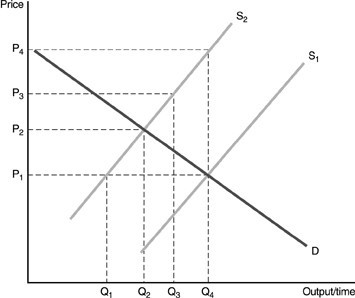 Refer to the above figure. S1 is the supply curve that includes only private costs. S2 is the supply curve that includes social costs. The free market rate of output is ________ and the corrected, socially optimal amount of output is ________.
Refer to the above figure. S1 is the supply curve that includes only private costs. S2 is the supply curve that includes social costs. The free market rate of output is ________ and the corrected, socially optimal amount of output is ________.
A. Q4; Q1 B. Q2; Q1 C. Q2; Q4 D. Q4; Q2