The monopolist, unlike the perfectly competitive firm, can continue to earn an economic profit in the long run because of:
a. collusive agreements with competitors.
b. price leadership.
c. cartels.
d. a dominant firm.
e. extremely high barriers to entry.
e
You might also like to view...
The great German hyperinflation during 1922-1923 can be attributed to the:
A) German government printing money to pay bills. B) absence of financial intermediaries in Germany. C) emergence of large number of monopolies in Germany. D) economic policy that restricted the import of goods into Germany.
Which of the following is the national security argument against free trade?
A) A country must protect firms from dumping by foreign companies. B) A country must protect new industries to give them a chance to mature before facing foreign competition. C) A country must protect its consumers from foreign influences. D) A country must protect industries that produce defense equipment and armaments. E) A country must preserve its jobs.
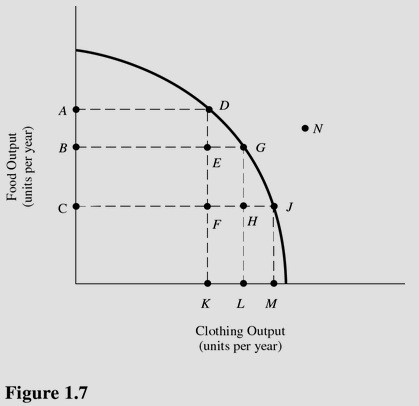 Refer to Figure 1.7. The cost of producing at point G rather than point D is
Refer to Figure 1.7. The cost of producing at point G rather than point D is
A. AB units of food. B. OA units of food. C. KL units of clothing. D. OL units of clothing.
Refer to the data. For the years shown, the growth of:
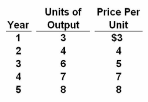
Assume an economy that makes only one product and that year 3 is the base year. Output and price data for a five-year period are as follows. Answer the question on the basis of these data.
A. real GDP has exceeded the growth of nominal GDP.
B. nominal GDP accurately reflects changes in real output.
C. nominal GDP overstates increases in real output.
D. nominal GDP understates increases in real output.