Michael Jordan averaged 35 points per game over a 100-game season. During the playoff round of 10 games, he averaged 50 points, and in the five-game championship series, he led the Chicago Bulls to victory, averaging 40 points. For the entire season, how many points did Jordan score, what was his average, and did the championship series pull his previous average up or down?
Over the regular season, Jordan scored 35 × 100 = 3,500 points. He added 500 points in the playoff, for a 4,000-point total over 110 games. His average rose to 36.3 . Since his "marginal" 40-point performance in the championship was above his average of 36.3, he pulled up his average. The season total was 4,200 points; his average was 4,200/115 = 36.5.
You might also like to view...
Based on the figure below. Starting from long-run equilibrium at point C, an increase in government spending that increases aggregate demand from AD to AD1 will lead to a short-run equilibrium at point ________ creating _____gap. 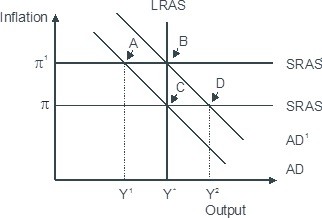
A. D; an expansionary B. B; no output C. B; expansionary D. A; a recessionary
Assume the market for cage-free eggs is perfectly competitive. All else equal, as more farmers choose to produce and sell cage-free eggs, what is likely to happen to the equilibrium price of the eggs and profits of these farmers in the long run?
A) The equilibrium price is likely to remain unchanged and profits are likely to increase. B) The equilibrium price is likely to decrease and profits are likely to decrease. C) The equilibrium price is likely to increase and profits are likely to increase. D) The equilibrium price is likely to increase and profits are likely to remain unchanged.
Since World War II, the share of total income going to the bottom 20 percent of U.S. households has
A) fallen by 20 percent. B) increased by 10 percent. C) remained constant. D) more than doubled.
The idea that any public information you will be able to find will prove of little value to you when buying and selling stocks, because that information is so quickly incorporated into the trading prices of stocks, is known as the
A) theory of efficient markets. B) theory of fundamental analysis. C) principle of context. D) over-the-counter hypothesis.