List and explain the functions of the regulatory molecules in a sarcomere, specifying how the on and off positions are controlled and its impact on the crossbridges formed.
What will be an ideal response?
Troponin and tropomyosin and the primary regulatory proteins. Tropomyosin wraps around the actin of the thin filament to restrict access of the myosin to its binding site on the actin molecule. When intracellular calcium concentration is low such that troponin is not bound by calcium (resting muscle), the tropomyosin is in the off position and myosin is weakly bound to actin (low force crossbridge). When muscle is stimulated, the increasing calcium binds to the troponin (C subunit) to shift the tropomyosin into the on position. In the on position, the
crossbridges that are formed are high force.
You might also like to view...
Primary active transport moves which of the following ions across the membrane?
a. sodium b. potassium c. hydrogen d. calcium e. all of these answers.
Which of the following movements is possible at the hip or coxal joint?
A. rotation B. flexion C. adduction D. circumduction E. All of these are possible.
The axons of the parasympathetic postganglionic neurons secrete ________.
A. epinephrine B. acetylcholine C. acetylcholine or epinephrine D. norepinephrine E. acetylcholine or norepinephrine
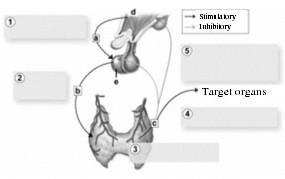 This figure shows an example of regulation of hormone secretion by a negative feedback loop. The large box labeled 1 represents the initial stimulus. Which could be the initial stimulus for this pattern of regulation?
This figure shows an example of regulation of hormone secretion by a negative feedback loop. The large box labeled 1 represents the initial stimulus. Which could be the initial stimulus for this pattern of regulation?
A. Low RBC (red blood cell) count B. Low body temperature C. Low blood sugar level D. High blood calcium level E. High WBC (white blood cell) count