Draw and explain the sigmoidal shape of the oxygen equilibrium curve for vertebrate hemoglobin. In your drawing, be sure to label your axes
What will be an ideal response?
Answer: Monomeric respiratory pigments, such as mammalian myoglobin, have a hyperbolic oxygen equilibrium curve because they do not bind oxygen cooperatively. Hemoglobins, on the other hand, are multimeric respiratory pigments. They display cooperative binding, which means that its affinity for oxygen changes with the amount of oxygen already bound. Hemoglobins are composed of two α and two β subunits that form two dimers that interact loosely with one another. When a hemoglobin molecule is fully deoxygenated, it is in the rigid T-state. It is stabilized by hydrogen bonds, binding of allosteric effectors, and salt bridges between the subunits. In this state, it has a relatively low affinity for oxygen; But when oxygen binds to one of the heme groups, the hemoglobin changes to an R-state, with an increased affinity for oxygen. The net effect of this cooperative binding is an oxygen equilibrium curve with a sigmoidal shape. The oxygen equilibrium curve should be drawn with PO2 on the x-axis, and percent saturation of hemoglobin on the y-axis.
You might also like to view...
The interstitial endocrine cells in the testes produce
A) dihydrotestosterone. B) androstenedione. C) growth hormone. D) progesterone. E) testosterone.
Birds transfer sperm directly from the __________ of the male to that of the female
Fill in the blank with the correct word.
Structure F is the
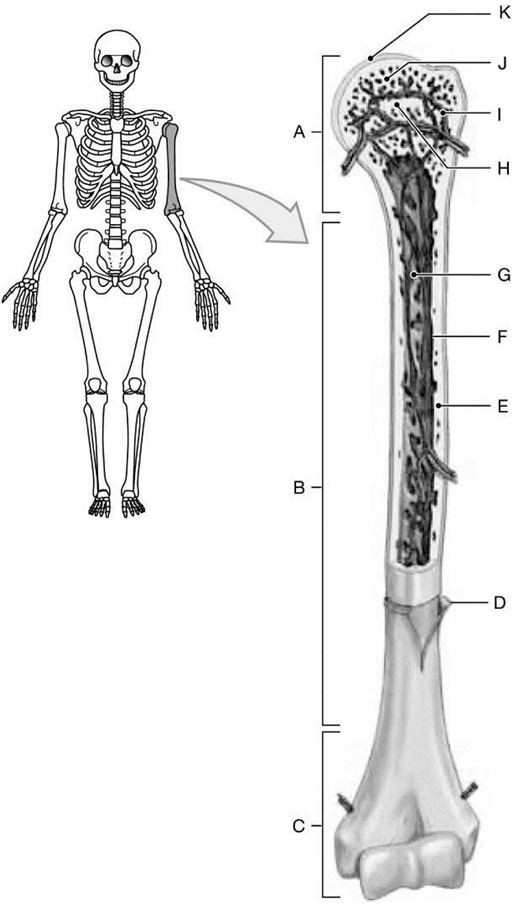
A) blood cavity.
B) epiphysis.
C) periosteum.
D) hyaline cartilage.
E) endosteum.
Cells regulate their level of activity by regulating the amount of proteins present in the cell at any given time, so an up regulation of enzymes would be expected to
A) increase the rate of reactions catalyzed by the enzymes. B) increase the level of productivity of chemical reactions that rely on them. C) decrease the rate of reactions catalyzed by the enzymes. D) decrease the level of productivity of chemical reactions that rely on them. E) both decrease the level of productivity of chemical reactions that rely on them and decrease the rate of reactions catalyzed by the enzymes.