An increase in the price of one good can cause the demand for another good to increase if the goods are complements.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)
False
If the price of a good increases, consumers will buy a lower quantity of that particular good along with fewer of the complementary goods regardless of the price of the complement.
You might also like to view...
A country undertakes a revaluation in order to
A) decrease its net exports. B) move to a flexible exchange rate system. C) lower the value at which its currency is pegged. D) increase its net exports.
Refer to the table below. Suppose the profit for each unit of paper product is $2.00 and the profit for each unit of lumber is $5 and Big Oaks is producing the profit-maximizing quantity of lumber and paper products. If the profit from each unit of paper product increases from $2 to $3 and the profit for each unit of lumber does not change, to maximize profit, Big Oaks should produce a ________
proportion of paper products and produce ________ units of paper products and lumber.
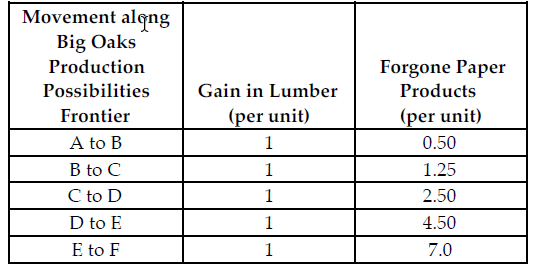
Big Oaks can produce either paper products or lumber with each tree that they harvest. Because Big Oaks can adjust the amount of paper products and lumber they produce from the harvested trees, paper products and lumber are produced in variable proportions. The above table summarizes Big Oaks production possibilities from each harvested tree.
A) smaller; less
B) smaller; more
C) greater; less
D) greater; more
An insurance policy is a contract that:
a. benefits the parties if they have the same degrees of risk aversion. b. benefits the parties if both of them are risk neutral. c. benefits the parties if they have different degrees of risk aversion. d. benefits the parties if either of them is risk neutral.
Which of the following would most likely reduce the number of bank failures?
a. an increase in the number of small banks b. tighter restrictions on interstate banking c. creating a system of deposit insurance d. encouraging banks to make more risky loans