The electric field 1.5 cm from a very small charged object points toward the object with a magnitude of 180,000 N/C. What is the charge on the object? (k = 1/4??0 = 8.99 × 109 N • m2/C2)
A) -4.5 nC
B) +4.5 nC
C) -5.0 nC
D) +5.0 nC
A
You might also like to view...
What is a shock front?
A) a wave of pressure that moves faster than the speed of sound B) a wave of pressure that moves slightly slower than the speed of sound C) a wave of pressure that moves faster than the speed of light D) a wave of electromagnetic energy that can create electrical shocks E) the wave created when protons slam into electrons
A cubical box 25.00 cm on each side is immersed in a fluid. The pressure at the top surface of the box is 109.4 kPa and the pressure on the bottom surface is 112 kPa. What is the density of the fluid?
A) 1000 kg/m3 B) 1030 kg/m3 C) 1060 kg/m3 D) 1090 kg/m3 E) 1120 kg/m3
When we look into the band of light in our sky that we call the Milky Way, can we see distant galaxies? Why or why not?
A) Yes, they appear as small, fuzzy patches on the other side of our galaxy. B) No, because there are only galaxies above and below the plane of the Milky Way. C) No, because the stars, gas, and dust of the Milky Way block us from seeing them. D) Yes, there are many other galaxies that we see inside the Milky Way.
The circuit below contains three 100-watt light bulbs and a capacitor. The emf ? = 110V. The capacitor is fully charged. Which light bulb(s) is(are) dimmest?
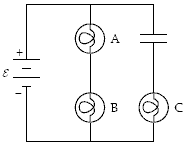
a.
A
b.
B
c.
C
d.
A and B
e.
All three are equally bright (or dim).