According to the income effect, an increase in the price of oranges will:
a. cause consumers to consume more apples because of greater savings on that good
b. cause consumers to spend more on oranges because a higher price signals that oranges are better than apples.
c. cause consumers to replace some oranges with other fruit that is now relatively cheaper than oranges.
d. leave consumers with less real income to spend on all goods.
d
You might also like to view...
Suppose the measured unemployment rate is 3.9% and the natural rate of unemployment is 5.1%. In this situation, policymakers should
A) attempt to stimulate the economy. B) attempt to slow the economy. C) not intervene in the economy. D) The actions of policymakers will depend on how much of the natural rate is frictional unemployment and how much is structural unemployment.
The difference between the interest a bank earns on loans and securities and the interest paid on deposits and debt divided by the total value of its assets is called
A) interest spread. B) net interest margin. C) return on assets. D) return on equity.
Who among the following individuals will not be a part of the U.S. labor force?
a. An unemployed computer worker who has given up looking for a job b. A college graduate seeking job after graduation c. An unemployed person who is not working because of a labor dispute d. A person who can work only part-time e. A person who recently moved to a new city and has not yet found a job
In Figure 45.4, when compared to the perfectly competitive equilibrium, the number of workers hired as a result of unionization 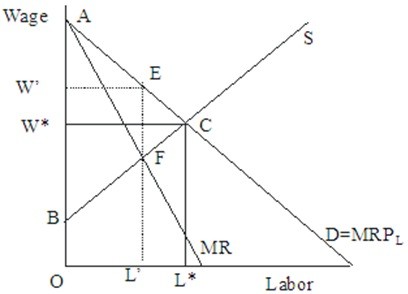 Figure 45.4
Figure 45.4
A. increases from L' to L*. B. remains at L'. C. remains at L*. D. decreases from L* to L'.