The analysis of how asymmetric information problems affect economic behavior is called ________ theory
A) uneven
B) parallel
C) principal
D) agency
D
You might also like to view...
As output increases, average total cost decreases
A) constantly. B) as the average product of labor decreases. C) initially and then starts to increase. D) in the long run and the short run. E) as long as average fixed cost decreases.
A natural monopoly is a market in which a single firm:
A. owns a key resource or input into the production of the good. B. gains market share over time through aggressive tactics. C. can produce the entire market quantity at a lower cost than multiple firms. D. is protected from competition through government legislation.
Which of the following does not constitute an act of "investment" as economists use the term?
A. An accountant attends a seminar on changes in the federal tax code. B. The city council authorizes the construction of a new fire station. C. A department store increases its inventory of football jerseys before the Super Bowl. D. A retiree buys 50 shares of stock at $10 a share and then sells the stock at a profit for $20 a share.
Refer to the information provided in Figure 2.5 below to answer the question(s) that follow.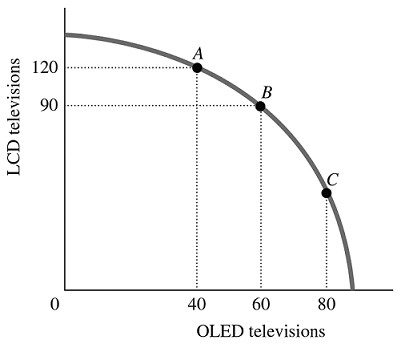 Figure 2.5Refer to Figure 2.5. The economy is currently at Point B. The opportunity cost of moving from Point B to Point A is the
Figure 2.5Refer to Figure 2.5. The economy is currently at Point B. The opportunity cost of moving from Point B to Point A is the
A. 120 LCD TVs that must be forgone to produce 20 additional OLED TVs. B. 30 LCD TVs that must be forgone to produce 40 additional OLED TVs. C. 20 OLED TVs that must be forgone to produce 30 additional LCD TVs. D. 40 OLED TVs that must be forgone to produce 120 additional LCD TVs.