An uncharged spherical conducting shell surrounds a charge ?q at the center of the shell. Then charge +3q is placed on the outside of the shell. When static equilibrium is reached, the charges on the inner and outer surfaces of the shell are, respectively,
A. +q, ?q.
B. ?q, +q.
C. +q, +2q.
D. +2q, +q.
E. +3q, 0.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
The ________ theory was based on the assumption that the universe was eternal and unchanging
a. inflationary b. accelerating c. steady-state d. big bang
Which of these uses thermal energy to do work?
A) a person walking uphill B) a hot air balloon C) an electric heater D) All of the above. E) None of the above.
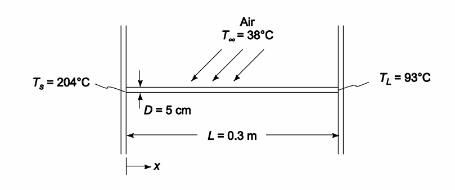
One end of a 0.3-m-long steel rod is connected to a wall at 204°C. The other end is connected to a wall that is maintained at 93°C. Air is blown across the rod so that a heat transfer coefficient of 17 W/(m2 K) is maintained over the entire surface. If the diameter of the rod is 5 cm and the temperature of the air is 38°C, what is the net rate of heat loss to the air?
GIVEN
FIND
The net rate of heat loss to the air (qf)
ASSUMPTIONS
The wall temperatures are constant
The system is in steady state
The rod is 1% carbon steel
The thermal conductivity of the rod is uniform and not dependent on temperature
One dimensional conduction along the rod
SKETCH
How does terrestrial radiation warm Earth's surface?
What will be an ideal response?