A temporary adverse productivity shock would
A. decrease the level of employment.
B. decrease the expected future marginal product of capital.
C. shift the labor supply curve upward.
D. decrease future income.
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
The process of research and development
A. always leads to useful products. B. almost never leads to useful products. C. often involves a waste of resources. D. is usually conducted in governmental laboratories.
Suppose that many consumers tend to over-state the discount rate that should be used for computing the net present value of education, just as they do when making investments in durable goods like cars and appliances
What would happen if consumers (as a group) started to use lower discount rates when making decisions about their education? A) NPV of a degree declines, demand for eduction declines B) NPV of a degree declines, demand for education increases C) NPV of a degree increases, demand for education declines D) NPV of a degree increases, demand for education increases
Suppose that there is a negative externality associated with alcohol consumption in the United States (e.g., costs of publicly funded alcoholism treatment centers). What will happen to the social costs of this externality if the United States eliminates all tariffs on alcohol imports?
a. The social coasts will increase. b. They will not change. c. They will decrease. d. The social costs will increase but be offset by the private losses associated with increased imports as the tariffs are eliminated.
Using Figure 1.4, we know the production of 6 units of soda and 2 units of pizza is 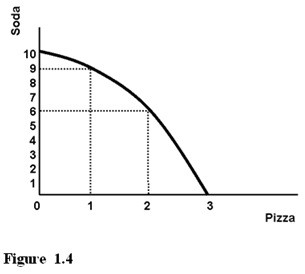
A. impossible because we have the resources but do not have the technology. B. impossible because we have the technology but do not have the resources. C. possible, but there would be unemployment. D. possible, but only if all resources were fully employed.