A 38-year-old woman is going to ovulate in about a week. For how long has the primary oocyte in her Graafian follicle been arrested at prophase I of meiosis?
A. 38 years
B. About a day
C. 1 week
D. 3 weeks
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
When Ron Evans generated transgenic mice in which the gene PPAR-delta was constituitively active (i.e., always expressed), he found that these mice showed a shift from fast glycolytic fibers to slow oxidative fibers. One consequence of this change was that the transgenic mice
A. showed greater endurance in a running test. B. showed less endurance in a running test. C. had leg muscles with lower mitochondrial and capillary densities than wild-type (nontransgenic) mice. D. were more likely to become obese than wild-type (nontransgenic) mice. E. had muscles that were not as red as those of wild-type (nontransgenic) mice.
This diagram illustrates the action of a proteasome on protein marked with ubiquitin tags. What statement about this process is true?
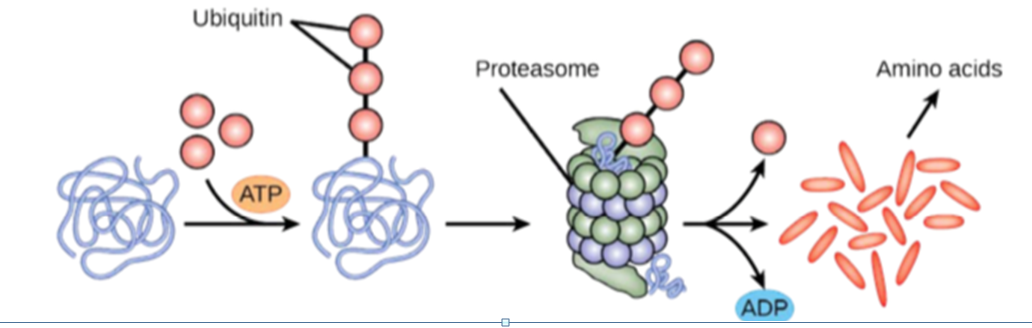
a. Degradation of proteins results in the destruction of the proteasome.
b. Degradation of proteins in proteasomes produces a net output of energy.
c. Degradation of proteins in proteasomes requires a net input of energy.
d. Proteasomes absorb all non-amino acid components of proteins.
Mycorrhizae
a. increase plant growth. b. are symbionts. c. concentrate nutrients they then share with plants. d. increase the surface area for absorption. e. are described by all of these.
Studies in knockout mice have demonstrated an important role of the FOXP2 transcription factor in the development of vocalizations
Recent sequence comparisons of the FOXP2 gene in Neanderthals and modern humans show that while the DNA sequence may be different, the protein sequence it codes for is identical. What might logically be inferred from this information? A) There was a problem with the experiment because different DNA sequences cannot result in the same protein sequence. B) The differences in DNA sequence support the hypothesis that Neanderthals were primitive beings that could only grunt. C) Human and Neanderthal vocalizations may have been more similar than previously thought. D) The experiments in mice demonstrating the function of the FOXP2 gene are not relevant to humans and Neanderthals because they are not primates.