Animals breathe in air containing oxygen and breathe out air with less oxygen. The consumed oxygen is used:
A. in the Krebs cycle.
B. in the glycolysis pathway.
C. in the conversion of pyruvate to acetyl Co-
A.
D. in photosynthesis.
E. as an electron acceptor in the respiratory
electron transport chain.
E
You might also like to view...
Are all fungi detrimental (bad) for other organisms?
A. Yes-think of molds that destroy plant crops, or fungal infections that cause athlete's foot. All fungi are bad for organisms they colonize. B. Yes-fungi feed directly on organic material (oftentimes killing it or feeding on it after the original organism has died). As such, they are always bad for other organisms. C. No-fungi are sometimes good, sometimes bad for other organisms. It really depends on which fungus you're talking about and the relationship it has with the other organism. Some fungi, for example, can form a symbiotic relationship with plant roots that increases their nutrient and water absorption. This is good. D. No-fungi are ALWAYS good when they interact with other organisms. There's never a downside or negative aspect to such interactions. Both sides always benefit from the relationship.
"We are only going to trace this one trait from one generation to another." This statement would indicate that
A. the researcher is not sure of how this trait is inherited. B. they will be developing a monohybrid (single factor) line. C. multiple alleles are involved here. D. a double-factor cross has been made.
Evolutionary change can occur when the frequency of alleles in a population changes. Which of the following describes a change in the allele frequency of a population due to chance?
A) founder effect B) bottleneck effect C) genetic drift D) gene flow
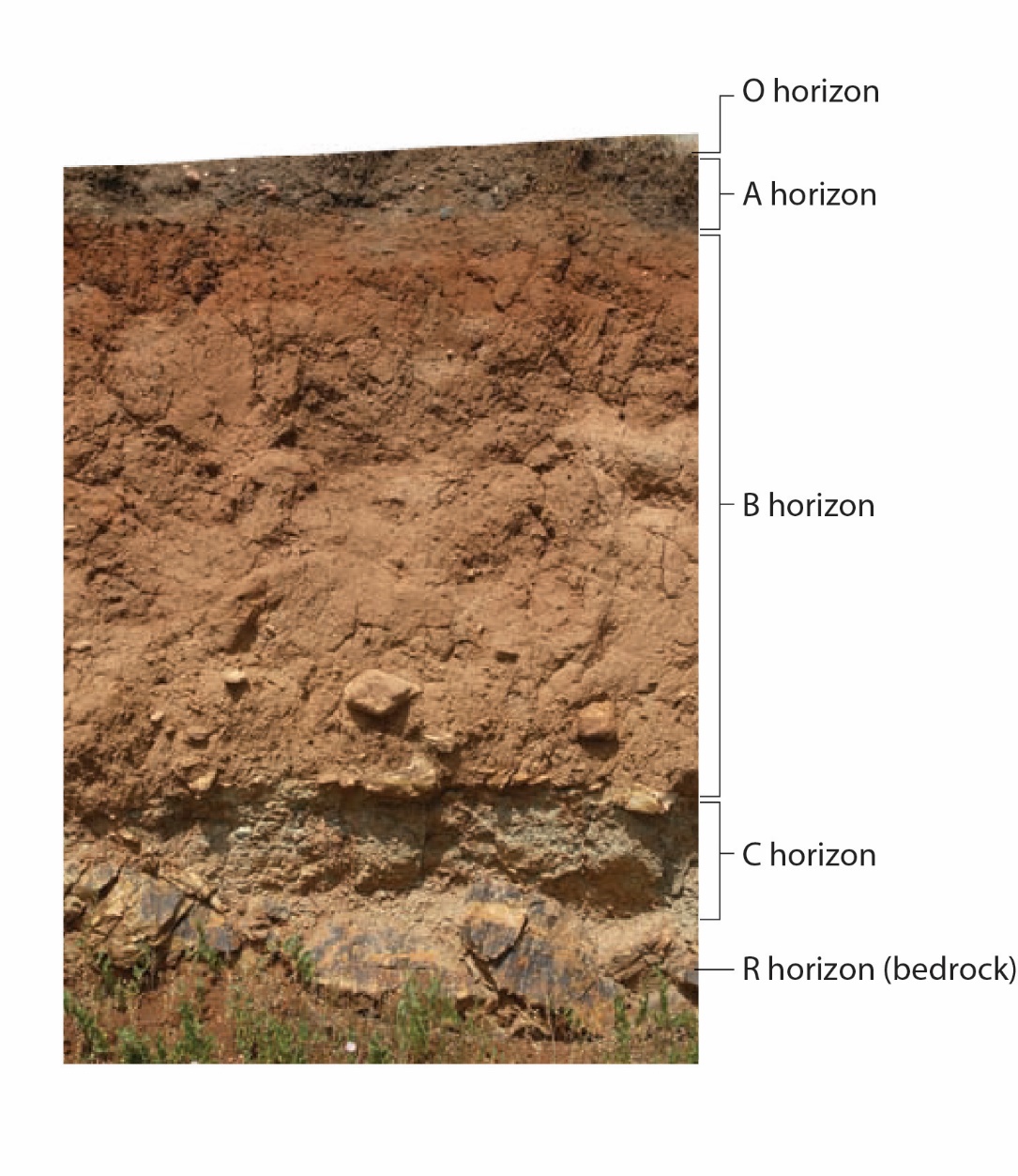
A. O Horizon B. A Horizon C. B Horizon D. C Horizon E. Bedrock