A scientist might create a conditional knockout of a mouse gene when
A) a homozygous loss-of-function mutation in the gene causes embryonic lethality.
B) a homozygous loss-of-function mutation in the gene produces a wild-type phenotype.
C) a homozygous loss-of-function mutation in the gene affects only ears.
D) a homozygous loss-of-function mutation in the gene affects only coat color.
A) a homozygous loss-of-function mutation in the gene causes embryonic lethality.
You might also like to view...
The atomic ratio of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen for most carbohydrates is:
a. 1:2:1 b. 1:2:2 c. 2:1:1 d. 2:1:2
Stomach motility
a. decreases following a heavy meal. b. moves chime through the pyloric sphincter. c. is unaffected by emotional state or external environmental factors. d. may be retarded when stretch receptors on the stomach wall are activated. e. is increased by hormones released in response to high stomach acidity
Figure 55-2 is a good illustration of:
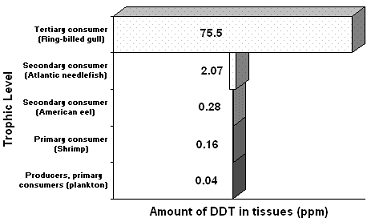
a. bioconcentration.
b. biological magnification.
c. persistence.
d. narrow-spectrum botanicals.
e. the pesticide treadmill.
Cross between an individual with a dominant phenotype and an individual with a recessive phenotype to determine whether the dominant individual is homozygous or heterozygous.
What will be an ideal response?