Suppose two demand curves intersect and so have a point in common. At that point, demand shown by the steeper curve will be ________ the flatter curve.
A. less elastic than
B. as elastic as
C. more elastic than
D. more likely to be unit elastic than
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
The figure below shows the foreign exchange market. D£ is the nonofficial demand curve for pounds. S£ (Spring-summer) and S£ (Autumn-winter) are the nonofficial supply curves of pounds during the spring-summer and autumn-winter seasons, respectively. Assume that the British government is committed to maintaining a fixed exchange rate at $1.90 per pound. In the Spring-summer period, what type of intervention must British monetary authorities engage in?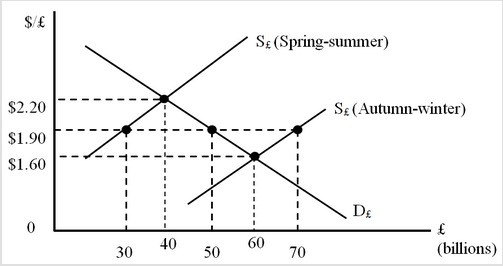
A. Sell 10 billion pounds at $2.20 B. Buy 40 billion pounds at $2.20 C. Buy 20 billion pounds at $1.90 D. Sell 20 billion pounds at $1.90
Using Figure 1 above, if the aggregate demand curve shifts from AD1 to AD2 the result in the long run would be: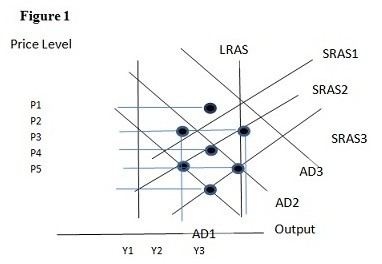
A. P1 and Y2. B. P2 and Y2. C. P3 and Y1. D. P2 and Y3.
Why have nations sought free-trade zones and economic integration with other nations? What is an example?
What will be an ideal response?
Refer to the diagram. Assume that G and T 1 are the relevant curves, the economy is currently at A, and the full-employment GDP is B. This economy has a(n):

A. cyclically adjusted budget deficit.
B. actual budget deficit.
C. actual budget surplus.
D. neither a surplus nor deficit in the actual budget.