The table gives data on the production and prices in a small economy. Use 2012 as the base period
a. What does nominal GDP equal in 2012?
b. What does real GDP equal in 2012?
c. What does nominal GDP equal in 2013?
d. Using the chained-price method, what does real GDP equal in 2013?
a. Nominal GDP in 2012 equals $8.00. Nominal GDP equals the sum of the market value of hot dogs ($6.00 ) plus the market value of Pepsi ($2.00 ).
b. Real GDP in 2012 equals $8.00. Real GDP equals nominal GDP in the base period.
c. Nominal GDP in 2013 equals $14.25. Nominal GDP equals the sum of the market value of hot dogs ($10.50 ) plus the market value of Pepsi ($3.75 ).
d. Real GDP in 2013 equals $12.00. To calculate real GDP in 2013, we need the percentage change in production between 2012 and 2013 valuing the production at 2012 prices and at 2013 prices. Both percentage changes are 50 percent. (For example, using 2012 prices, production in 2012 is $8.00 and in 2013 is $12.00, a 50 percent increase.) Because both percentage changes are 50 percent, the average production change is 50 percent. Therefore real GDP in 2013 equals real GDP in 2012 multiplied by 150 percent, or ($8.00 × 1.50 ) = $12.00.
You might also like to view...
Consider the utility function 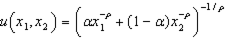
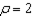
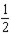
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)
If a monopolist's price is $50 at the output where marginal revenue equals marginal cost and average total cost is $43, then the average profit is $7
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Which of the following is not considered part of M2?
A. small time deposits of less than $100,000 B. money market mutual fund shares C. savings deposits D. large time deposits of more than $100,000
When oligopolistic companies engage in collusion, the companies are involved in a
A. noncooperative game. B. competitive game. C. cooperative game. D. negative-sum game.