A fluid flows at 5 m/s over a wide, flat plate 15-cm-long. For each of the following list, calculate the Reynolds number at the downstream end of the plate. Indicate weather the flow at that point is laminar, transition, or turbulent. Assume all fluids are at 40°C.
(a) Air
(b) CO2
(c) Water
(d) Engine Oil
GIVEN
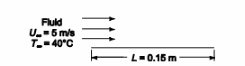
A fluid flows over a flat plate
Fluid velocity (U?) = 5 m/s
Length of plate (L) = 15 cm = 0.15 m
Fluid temperature = 40°C
FIND
The Reynolds number at the downstream end of the plate (ReL) for
(a) Air
(b) CO2
(c) Water
(d) Engine Oil
Indicate if the flow is laminar, transitional, or turbulent
ASSUMPTIONS
Steady state
SKETCH
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
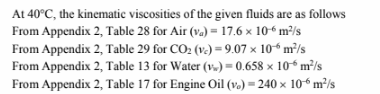
The Reynolds number, from Table 5.3, is
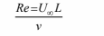
The transition from laminar to turbulent flow over a plate occurs at a Reynolds number of about
5 x 105. For air
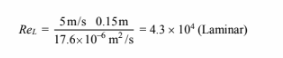
For CO2
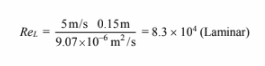
For water
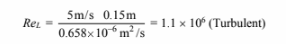
For engine oil
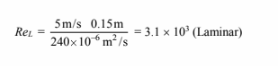
You might also like to view...
A magnifying glass uses a convex lens with a refractive power of 20 diopters. What is the angular magnification if the image is to be viewed by a relaxed eye with a near point of 25 cm?
A) 5.0 B) 3.0 C) 4.0 D) 1.0 E) 2.0
The great variety of igneous rocks is due to _______.
Fill in the blank(s) with the appropriate word(s)
Which of the following stars has a spectrum that peaks at the highest frequency?
A) a blue star B) a red star C) a yellow star
A supercluster is a ________.
A. group of open star clusters B. cluster of several dozen galaxy clusters C. group of globular star clusters D. All of these choices are correct.