Gas at constant T and P is contained in a supply line connected through a valve to a closed tank containing the same gas at a lower pressure. The valve is opened to allow flow of gas into the tank, and then is shut again.
(a) Develop a general equation relating 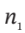 and
and 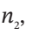 the moles (or mass) of gas in the tank at the beginning and end of the process, to the properties
the moles (or mass) of gas in the tank at the beginning and end of the process, to the properties 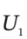 and
and 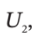 the internal energy of the gas in the tank at the beginning and end of the process, and H?, the enthalpy of the gas in the supply line, and to Q, the heat transferred to the material in the tank during the process.
the internal energy of the gas in the tank at the beginning and end of the process, and H?, the enthalpy of the gas in the supply line, and to Q, the heat transferred to the material in the tank during the process.
(b) Reduce the general equation to its simplest form for the special case of an ideal gas with constant heat capacities.
(c) Further reduce the equation of (b) for the case of 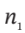 = 0.
= 0.
(d) Further reduce the equation of (c) for the case in which, in addition, Q = 0.
(e) Treating nitrogen as an ideal gas for which 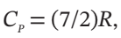 apply the appropriate equation to the case in which a steady supply of nitrogen at 25°C and 3 bar flows into an evacuated tank of 4
apply the appropriate equation to the case in which a steady supply of nitrogen at 25°C and 3 bar flows into an evacuated tank of 4 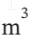 volume, and calculate the moles of nitrogen that flow into the tank to equalize the pressures for two cases:
volume, and calculate the moles of nitrogen that flow into the tank to equalize the pressures for two cases:
1. Assume that no heat flows from the gas to the tank or through the tank walls.
2. Assume that the tank weighs 400 kg, is perfectly insulated, has an initial temperature of 25°C, has a specific heat of 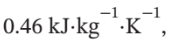 and is heated by the gas so as always to be at the temperature of the gas in the tank.
and is heated by the gas so as always to be at the temperature of the gas in the tank.
a. We can write a mole balance on the material in the tank as
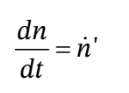
where 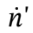 is the molar flow rate of gas entering the tank. This is (for this non-reacting system) equivalent to the mass balance
is the molar flow rate of gas entering the tank. This is (for this non-reacting system) equivalent to the mass balance 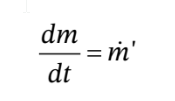 and can be obtained from it by simply dividing by the molecular weight of the gas.
and can be obtained from it by simply dividing by the molecular weight of the gas.
The corresponding energy balance is
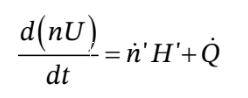
where we have written this using the molar flow rate and the molar enthalpy and internal energy. This differs in form from where we wrote it in terms of the mass flow rate and specific enthalpy and internal energy. Also, we have not assumed that the tank is adiabatic, so this equation has a heat flow term in it. However, we have assumed that the tank is rigid, so there is no non-flow work term.
We can combine the energy and mole balances to get
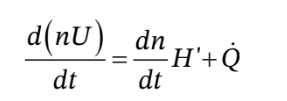
and we can integrate this over an arbitrary time interval (from time 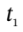 to time
to time 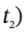 to get
to get
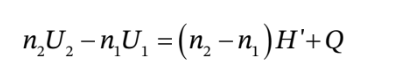 where Q is the total amount of heat that flows into the tank during the time interval from
where Q is the total amount of heat that flows into the tank during the time interval from 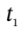 to
to 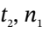 and
and 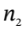 are the number of moles of gas in the tank at times
are the number of moles of gas in the tank at times 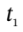 and
and 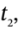 and
and 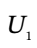 and
and 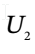 are the molar internal energy of the gas in the tank at times
are the molar internal energy of the gas in the tank at times 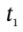 and
and 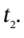 This can also be written as
This can also be written as 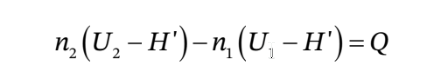
b. For an ideal gas with constant heat capacities, 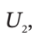 - H' can be written as
- H' can be written as
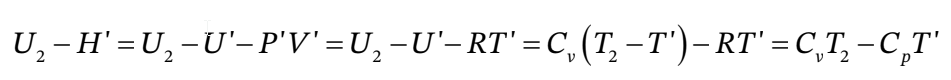
and likewise for 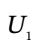 - H' , so
- H' , so
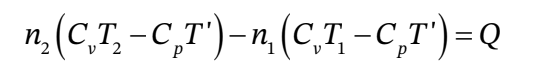
c. If 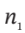 is zero, then this is just
is zero, then this is just 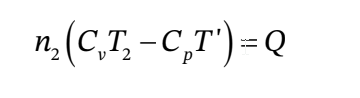
d. If Q is zero, then this is
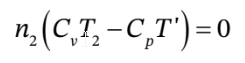
or
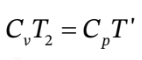
or
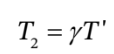
e. 1. This corresponds to the case in part (d) where the temperature in the tank is given by
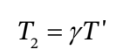
with ? = 1.4, so if the supply temperature is 298 K, the temperature of the gas in the tank will be 1.4*298 K = 417.2 K. When the pressure in the tank is equal to the supply pressure, gas will stop flowing. At 3 bar and 417.2 K the ideal gas law tells us that the number of moles in the tank will be
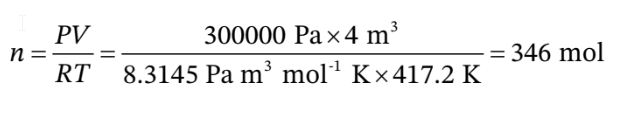
e. 2. The heat transferred to the tank is 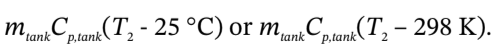 The heat transferred to the gas is the negative of this, so we have
The heat transferred to the gas is the negative of this, so we have 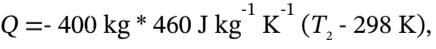 with
with 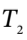 in K.Using this with the result from part (c) gives
in K.Using this with the result from part (c) gives 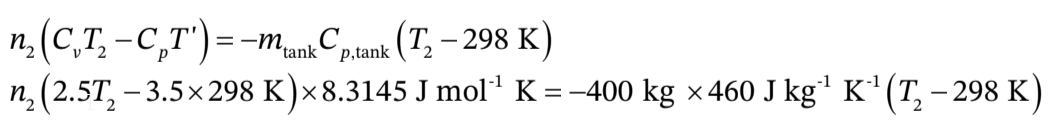
We also know that
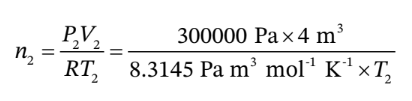
Substituting this in the previous equation gives us an equation for  alone (without
alone (without 
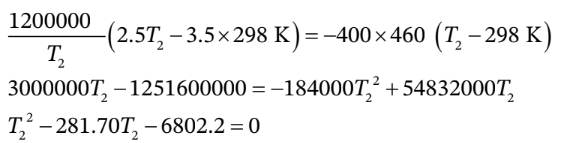
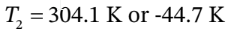 (of course only the first answer is physically meaningful)
(of course only the first answer is physically meaningful)
So then if the final temperature is 304.1 K, the final number of moles is
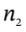 = 1200000/(8.31451*304.1) = 475 mol
= 1200000/(8.31451*304.1) = 475 mol
This is substantially more than in the previous part, because the temperature rise is small, because the heat capacity of the tank is very large compared to the heat capacity of the gas.
You might also like to view...
Technician A says that in a conventional flow cooling system, coolant leaves the engine through the top radiator hose. Technician B says that if cold water is added to a hot cooling system, the coolant pump could start to leak. Who is right?
A. ?Technician A only B. ?Technician B only C. ?Both A and B D. ?Neither A nor B
Which term best describes fish?
A) ectothermic B) endothermic C) heliothermic D) normothermic
Which technique is most commonly used for controlling the arc length when making a GTAW??
What will be an ideal response?
The ____ circuit supplies the initial current for the field coil that starts the buildup of the magnetic field.
A. starter B. excitation C. preexcitation D. charging