In the United States, barriers to entry in professional team sports (for example, football and baseball) result from
A) the draft of college players, which grants teams exclusive signing rights to individual players.
B) long-term leases teams sign for stadiums and ballparks in major cities.
C) the reserve clause, which is a provision in contracts of professional athletes that require them to play for specific teams over the length of their contracts.
D) television contracts, which give networks the exclusive rights to broadcast games.
B
You might also like to view...
(Requires Internet Access for the test question) The following question requires you to download data from the internet and to load it into a statistical package such as STATA or EViews
a. Your textbook estimates an AR(1) model (equation 14.7) for the change in the inflation rate using a sample period 1962:I — 2004:IV. Go to the Stock and Watson companion website for the textbook and download the data "Macroeconomic Data Used in Chapters 14 and 16." Enter the data for consumer price index, calculate the inflation rate, the acceleration of the inflation rate, and replicate the result on page 526 of your textbook. Make sure to use heteroskedasticity-robust standard error option for the estimation. b. Next find a website with more recent data, such as the Federal Reserve Economic Data (FRED) site at the Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis. Locate the data for the CPI, which will be monthly, and convert the data in quarterly averages. Then, using a sample from 1962:I — 2009:IV, re-estimate the above specification and comment on the changes that have occurred. c. Based on the BIC, how many lags should be included in the forecasting equation for the change in the inflation rate? Use the new data set and sample period to answer the question. What will be an ideal response?
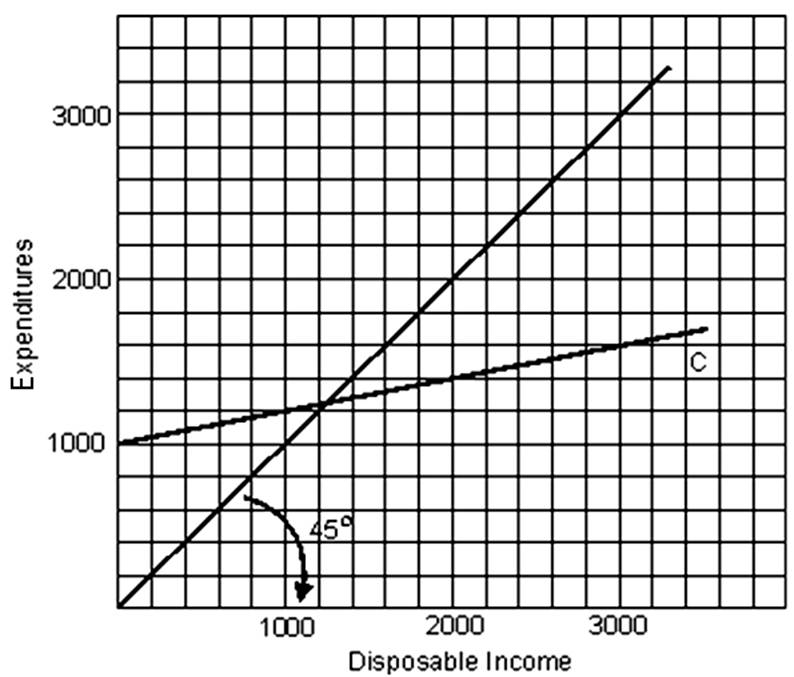
When disposable income is 1000, how much is consumption?
What fraction of this tax is borne by the workers?
Suppose the supply of labor is W – t = 10H, where W is the gross wage, t is the tax (in dollars), and H is labor hours. The demand for labor is W = 120 – 2H. a) 1/6 b) 2/6 c) 3/6 d) 4/6 e) 5/6
An increase in population growth in a country
A. may not necessarily cause an increase in per capita real Gross Domestic Product (GDP). B. may not cause an increase in labor resources in rich countries because employers will cut down on the number of hours required of workers. C. will always cause an increase in per capita real Gross Domestic Product (GDP). D. always causes an increase in labor resources.