Consider the market demand and supply given by the following: Qd=50 - P and Qs = 2.5 + 1.5P.
a) What is the equilibrium price and quantity?
b) If the government sets a price floor of $25, what is the surplus/shortage? If the government buys the surplus, what would be the cost to the government?
Answer :
A) Given,
Demand : Q = 50 - P
Supply : Q = 2.5 + 1.5P
At market equilibrium condition, Demand = Supply.
=> 50 - P = 2.5 + 1.5P
=> 50 - 2.5 = 1.5P + P
=> 47.5 = 2.5P
=> P = 47.5 / 2.5
=> P = 19
By putting P = 19 in demand function we get,
Q = 50 - 19 = 31
Therefore, the equilibrium price is P = $19 and the equilibrium quantity is Q = 31 units.
B) Now, because of price floor the price becomes, P= $25.
By putting P = $25 in demand function and supply function we get,
Demand : Q = 50 - 25 = 25
Supply : Q = 2.5 + 1.5×25 = 40
Surplus = Supply - Demand = 40 - 25 = 15 units.
Therefore, at P = $25 the market faces surplus of 15 units.
As government decided price floor level is $25 and the market surplus amount is 15 units and if this surplus amount is purchased by the government then the government has to pay $25 for each unit. Therefore, the total cost of purchasing surplus amount by the government becomes,
Government cost = $25 × 15 = $375 .
You might also like to view...
Refer to the figure below.________ inflation will eventually move the economy pictured in the diagram from short-run equilibrium at point ________ to long-run equilibrium at point ________. 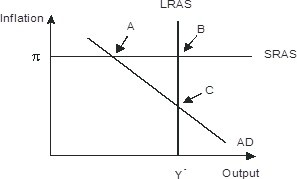
A. Rising; A B. Falling; A; C C. Falling; B: C D. Rising; A; C
The consumption function shows that when disposable income increases by one dollar, consumption expenditure
A) does not change. B) increases by more than a dollar. C) increases by one dollar. D) decreases by less than a dollar. E) increases by less than a dollar.
Marginal revenue product is measured by
a. MR × price of the good b. MR × MC c. TR / MPP d. MPP × price of the good e. TC / MPP
The fraction of additional income that households will spend on consumption is called;
(a) The marginal propensity to consume; (b) The average propensity to consume; (c) The Keynesian multiplier; (d) All of the above.