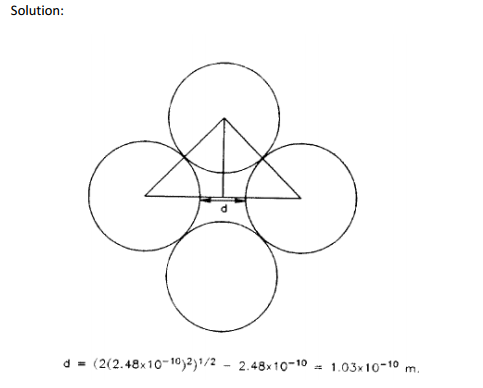
At room temperature, the stable crystal structure of iron is bcc. However, above 1183 K it becomes fcc. The iron fcc crystal structure is able to dissolve a much larger concentration of carbon than is the bcc structure. A primary reason for this is believed to be, that while the fcc structure is more close packed, the octahedral sites in the fcc lattice are much larger than the sites occupied by the carbon atoms in the bcc structure. The hole at the center of the fcc unit cell is such a site. See Fig. 1A. The minimum opening in one of these sites corresponds to the distance between atoms along a <100> direction. Note: that this is the same type of site as in the bcc case. Compare the fcc opening with that of the bcc lattice. For the sake of convenience, assume that the iron atom
diameter is the same as that of the bcc atom at room temperature.
What will be an ideal response?
Trades & Technology
You might also like to view...
A concrete finish that can be made to look like brick or stone is called
What will be an ideal response?
Trades & Technology
Degus, both male and female, are sexually mature _____ of age
a. prior to two months b. between 12 and 16 weeks c. at one year d. at approximately 4 weeks
Trades & Technology
Coolant can be checked using ________
A) Visual inspection B) Test strips C) Boiling/freezing points using a refractometer and hydrometer D) All of the above
Trades & Technology
Hubless cast iron is joined using
A. caulked joints B. compression joint gaskets C. neoprene gasket and stainless steel sleeve and clamps D. threaded joint
Trades & Technology