In the aggregate expenditures model, a decrease in government spending causes a(n):
a. upward shift in the aggregate expenditures curve.
b. downward shift in the aggregate expenditures curve.
c. shift in the 45-degree line.
d. rightward movement along the aggregate expenditures curve.
e. leftward movement along the aggregate expenditures curve.
b
You might also like to view...
The top policy goal for Paul Volcker when he became chairman of the Federal Reserve's Board of Governors in 1979 was
A) increasing regulation of commercial banks. B) increasing employment. C) a low current account deficit. D) fighting inflation. E) increasing economic growth.
High unemployment is undesirable because it
A) results in a loss of output. B) always increases inflation. C) always increases interest rates. D) reduces idle resources.
Suppose a market basket of goods and services costs $400 in the base year and $500 this year. The consumer price index (CPI) for this year is:
a. 25. b. 100. c. 125. d. 500.
Build-Right Concrete Products produces specialty cement used in construction of highways. Build-Right is a price-setting firm and estimates the demand for its cement by the State Highway Department using a demand function in the nonlinear form:Q = aPbMc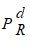 where Q = yards of cement demanded monthly, P = the price of Build-Right's cement per yard, M = state tax revenues per capita, and PR = the price of asphalt per yard. The manager at Build-Right transforms the nonlinear relation into a linear relation for estimation. The estimation results are presented below:
where Q = yards of cement demanded monthly, P = the price of Build-Right's cement per yard, M = state tax revenues per capita, and PR = the price of asphalt per yard. The manager at Build-Right transforms the nonlinear relation into a linear relation for estimation. The estimation results are presented below: 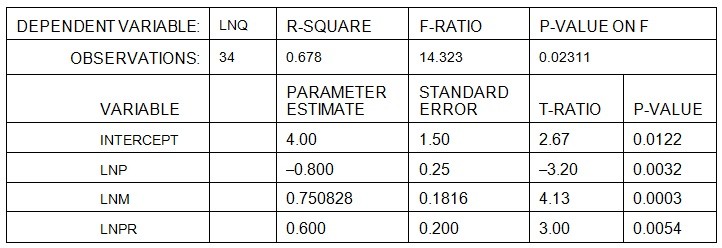
height="198" width="577" />Given the above, the estimated cross-price elasticity of demand for cement relative to the price of asphalt is A. 0.6 B. 0.3 C. 1.2 D. 3.0 E. none of the above